The use of Nanotrap particles for biodefense and emerging infectious disease diagnostics
- PMID: 24449537
- PMCID: PMC7108521
- DOI: 10.1111/2049-632X.12136
The use of Nanotrap particles for biodefense and emerging infectious disease diagnostics
Abstract
Detection of early infectious disease may be challenging due to the low copy number of organisms present. To overcome this limitation and rapidly measure low concentrations of the pathogen, we developed a novel technology: Nanotrap particles, which are designed to capture, concentrate, and protect biomarkers from complex biofluids. Nanotrap particles are thermoresponsive hydrogels that are capable of antigen capture through the coupling of affinity baits to the particles. Here, we describe recent findings demonstrating that Nanotrap particles are able to capture live infectious virus, viral RNA, and viral proteins. Capture is possible even in complex mixtures such as serum and allows the concentration and protection of these analytes, providing increased performance of downstream assays. The Nanotrap particles are a versatile sample preparation technology that has far reaching implications for biomarker discovery and diagnostic assays.
Keywords: Rift Valley fever virus; Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus; diagnostics; influenza.
© 2014 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




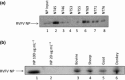
References
-
- Abdelwhab EM et al (2011) The use of FTA(R) filter papers for diagnosis of avian influenza virus. J Virol Methods 174: 120–122. - PubMed
-
- Baigent SJ & McCauley JW (2003) Influenza type A in humans, mammals and birds: determinants of virus virulence, host‐range and interspecies transmission. BioEssays 25: 657–671. - PubMed
-
- Banoo S et al (2010) Evaluation of diagnostic tests for infectious diseases: general principles. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(suppl 12): S17–S29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

