Population pharmacokinetic assessment of the effect of food on piperaquine bioavailability in patients with uncomplicated malaria
- PMID: 24449770
- PMCID: PMC4023753
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02318-13
Population pharmacokinetic assessment of the effect of food on piperaquine bioavailability in patients with uncomplicated malaria
Abstract
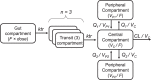
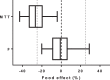
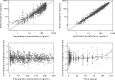
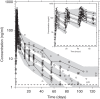
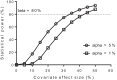
Previously published literature reports various impacts of food on the oral bioavailability of piperaquine. The aim of this study was to use a population modeling approach to investigate the impact of concomitant intake of a small amount of food on piperaquine pharmacokinetics. This was an open, randomized comparison of piperaquine pharmacokinetics when administered as a fixed oral formulation once daily for 3 days with (n=15) and without (n=15) concomitant food to patients with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Thailand. Nonlinear mixed-effects modeling was used to characterize the pharmacokinetics of piperaquine and the influence of concomitant food intake. A modified Monte Carlo mapped power approach was applied to evaluate the relationship between statistical power and various degrees of covariate effect sizes of the given study design. Piperaquine population pharmacokinetics were described well in fasting and fed patients by a three-compartment distribution model with flexible absorption. The final model showed a 25% increase in relative bioavailability per dose occasion during recovery from malaria but demonstrated no clinical impact of concomitant intake of a low-fat meal. Body weight and age were both significant covariates in the final model. The novel power approach concluded that the study was adequately powered to detect a food effect of at least 35%. This modified Monte Carlo mapped power approach may be a useful tool for evaluating the power to detect true covariate effects in mixed-effects modeling and a given study design. A small amount of food does not affect piperaquine absorption significantly in acute malaria.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. 2012. World malaria report 2012. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
-
- Zwang J, Ashley EA, Karema C, D'Alessandro U, Smithuis F, Dorsey G, Janssens B, Mayxay M, Newton P, Singhasivanon P, Stepniewska K, White NJ, Nosten F. 2009. Safety and efficacy of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine in falciparum malaria: a prospective multi-centre individual patient data analysis. PLoS One 4:e6358. 10.1371/journal.pone.0006358 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. 2010. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria, 2nd ed. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
-
- Tarning J, Zongo I, Some FA, Rouamba N, Parikh S, Rosenthal PJ, Hanpithakpong W, Jongrak N, Day NP, White NJ, Nosten F, Ouedraogo JB, Lindegardh N. 2012. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piperaquine in children with uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 91:497–505. 10.1038/clpt.2011.254 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tarning J, Ashley EA, Lindegardh N, Stepniewska K, Phaiphun L, Day NP, McGready R, Ashton M, Nosten F, White NJ. 2008. Population pharmacokinetics of piperaquine after two different treatment regimens with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine in patients with Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Thailand. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52:1052–1061. 10.1128/AAC.00955-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

