Beverage intake in early childhood and change in body fat from preschool to adolescence
- PMID: 24450382
- PMCID: PMC3922282
- DOI: 10.1089/chi.2013.0004
Beverage intake in early childhood and change in body fat from preschool to adolescence
Abstract
Background: Childhood obesity is closely associated with adult obesity, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. This study's aim was to determine the effects of beverage intake patterns on body composition from early childhood into adolescence in the Framingham Children's Study.
Methods: Multiple sets of 3-day records were used to assess diet over 12 years, beginning in 1987, in 103 non-Hispanic white boys and girls. BMI, waist circumference, and four skinfolds (triceps, subscapular, suprailiac, and abdominal) were measured yearly. Percent body fat was assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry at end of follow-up. Analysis of covariance and longitudinal mixed modeling were used to control for potential confounding by age, baseline body fat, percent of energy from fat, television/video viewing time, other beverage intakes not included in exposure group, mother's education, and BMI.
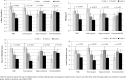
Results: Children with the lowest milk intakes in early childhood had 7.4% more body fat in later adolescence than those with higher intakes (30.0% body fat in tertile 1 vs. 22.6% in tertile 3; p=0.0095). Fruit and vegetable juice was similarly protective-those in the highest tertile of fruit and vegetable juice intake during childhood had an 8.0-cm smaller waist circumference at 15-17 years of age, compared with those in the lowest tertile (p=0.0328). There was no relation between sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) and percent body fat (p=0.9296) or other outcomes.
Conclusions: These results suggest that adequate intakes of milk and fruit and vegetable juice may reduce the risk of excess body fat in later childhood and adolescence. Further, modest intakes of SSBs in early childhood may not adversely affect body fat change.
Figures
References
-
- Freedman DS, Khan LK, Dietz WH, et al. . Relationship of childhood obesity to coronary heart disease risk factors in adulthood: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Pediatrics 2001;108:712–718 - PubMed
-
- Troiano RP, Flegal KM, Kuczmarski RJ, et al. . Overweight prevalence and trends for children and adolescents. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1963 to 1991. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1995;149:1085–1091 - PubMed
-
- Strauss RS, Pollack HA. Epidemic increase in childhood overweight, 1986–1998. JAMA 2001;286:2845–2848 - PubMed
-
- Hedley AA, Ogden CL, Johnson CL, et al. . Prevalence of overweight and obesity among US children, adolescents, and adults, 1999–2002. JAMA 2004;291:2847–2850 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical