Synthesis, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of new methyl-imidazolyl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles and 1,2,4-triazoles
- PMID: 24450412
- PMCID: PMC3914383
- DOI: 10.1186/2008-2231-22-22
Synthesis, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of new methyl-imidazolyl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles and 1,2,4-triazoles
Abstract
Background: Long-term clinical employment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is associated with significant side effects including gastrointestinal (GI) lesions and kidney toxicity. In this paper we designed and synthesized new imidazolyl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles and 1,2,4-triazoles by molecular hybridization of previously described anti-inflammatory compounds in the hope of obtaining new safer analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents.
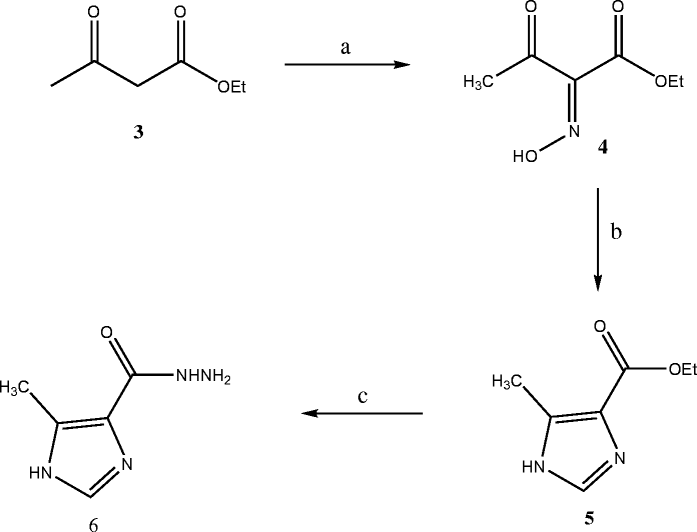
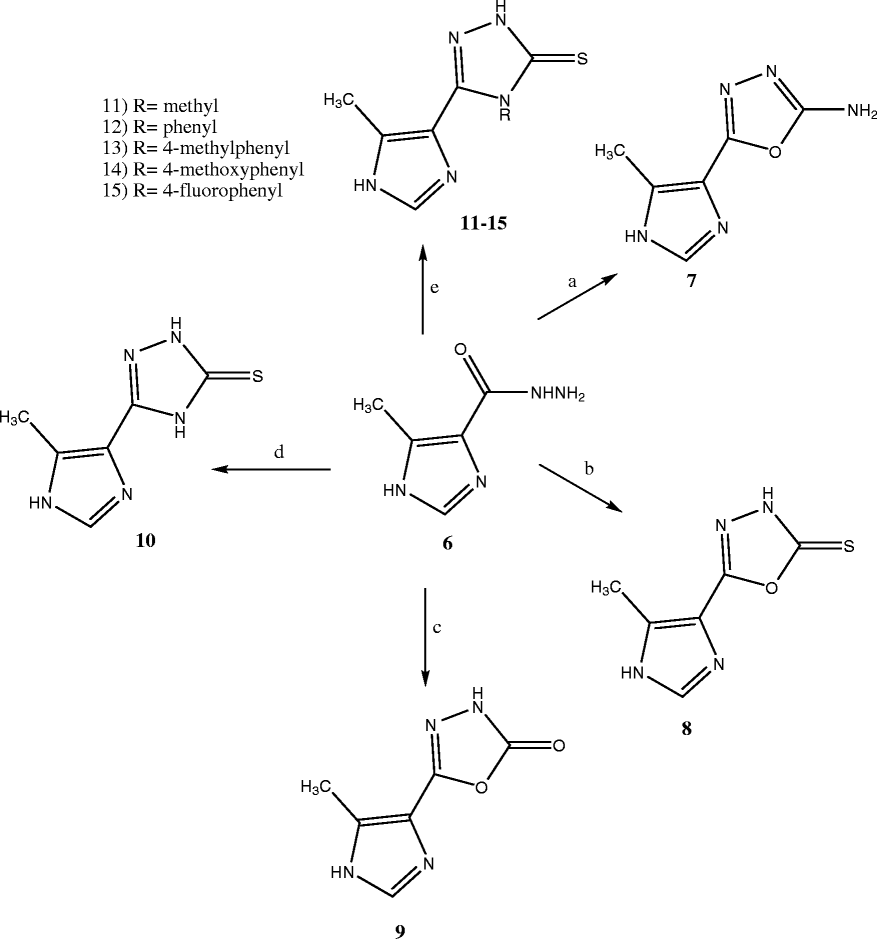
Methods: The target structures were synthesized by preparation of 5-methyl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 5. The reaction of hydrazine hydrate with this ester afforded the 5-methyl-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylic acid hydrazide 6 which was converted to target compounds 7-15 according to the known procedures. In silico toxicity risk assessment and drug likeness predictions were done, in order to consider the privileges of the synthesized structures as drug candidates.
Results and discussion: The analgesic and anti-inflammatory profile of the synthesized compounds were evaluated by writhing and carrageenan induced rat paw edema tests respectively. Compounds 8, 9 and 11-13 and 15 were active analgesic agents and compounds 8, 9 and 11-13 showed significant anti-inflammatory response in comparison with control. Compounds 11 and 13 were screened for their ulcerogenic activities and none of them showed significant ulcerogenic activity. The active Compounds 11 and 12 showed the highest drug likeness and drug score.
Conclusions: The analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of title compounds were comparable to that of standard drug indomethacin with a safer profile of activity. The results revealed that both of oxadiazole and triazole scaffolds can be determined as pharmacophores. The in silico predictions and pharmacological evaluations showed that compounds 11 and 12 can be chosen as lead for further investigations.
Figures
References
-
- Pontiki E, Hadjipavlou-Litina D, Litinas K, Nicolotti O, Carotti A. Design, synthesis and pharmacobiological evaluation of novel acrylic acid derivatives acting as lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitors with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. EurJ Med Chem. 2011;46(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.10.035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eleftheriou P, Geronikaki A, Hadjipavlou-Litina D, Vicini P, Filz O, Filimonov D, Poroikov V, Shailendra S, Chaudhaery E, Roy KK, Saxena AK. Fragment-based design, docking, synthesis, biological evaluation and structure–activity relationships of 2-benzo/benzisothiazolimino-5-aryliden-4-thiazolidinones as cycloxygenase/lipoxygenase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2012;47:111–124. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

