AMPK: a cellular energy sensor primarily regulated by AMP
- PMID: 24450630
- PMCID: PMC5703408
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20130244
AMPK: a cellular energy sensor primarily regulated by AMP
Abstract
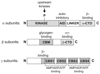
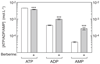
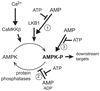
AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is a cellular energy sensor that monitors the ratio of AMP/ATP, and possibly also ADP/ATP, inside cells. Once activated by falling cellular energy levels, it acts to restore energy homoeostasis by switching on catabolic pathways that generate ATP, while switching off anabolic pathways and other processes consuming ATP. AMPK is switched on by increases in AMP via three mechanisms, all of which are antagonized by ATP: (i) promotion of phosphorylation of Thr172 by upstream activating kinases; (ii) inhibition of dephosphorylation of Thr172 by phosphatases; and (iii) allosteric activation of the phosphorylated kinase. Recently, it has been proposed that the first two mechanisms are also triggered by ADP, which might be the physiological signal rather than AMP, and that the third mechanism may not be physiologically significant. We have re-evaluated these questions, and found that only mechanism (ii) is mimicked by ADP, and that ADP is also less potent than AMP, which we still believe to be the primary signal. We have also provided evidence that mechanism (iii), i.e. allosteric activation by AMP, is a quantitatively significant mechanism in intact cells.
Figures
References
-
- Carlson CA, Kim KH. Regulation of hepatic acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1973;248:378–380. - PubMed
-
- Beg ZH, Allmann DW, Gibson DM. Modulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme: A reductase activity with cAMP and with protein fractions of rat liver cytosol. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 1973;54:1362–1369. - PubMed
-
- Yeh LA, Lee KH, Kim KH. Regulation of rat liver acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Regulation of phosphorylation and inactivation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by the adenylate energy charge. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:2308–2314. - PubMed
-
- Ingebritsen TS, Lee H, Parker RA, Gibson DM. Reversible modulation of the activities of both liver microsomal hydroxymethylglutaryl Coenzyme A reductase and its inactivating enzyme. Evidence for regulation by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 1978;81:1268–1277. - PubMed
-
- Ferrer A, Caelles C, Massot N, Hegardt FG. Activation of rat liver cytosolic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A reductase kinase by adenosine 5'-monophosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Comm. 1985;132:497–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

