Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 24450857
- PMCID: PMC4161365
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1315226
Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
Background: Patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have clinically significant coexisting medical conditions are less able to undergo standard chemotherapy. Effective therapies with acceptable side-effect profiles are needed for this patient population.
Methods: In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study, we assessed the efficacy and safety of idelalisib, an oral inhibitor of the delta isoform of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, in combination with rituximab versus rituximab plus placebo. We randomly assigned 220 patients with decreased renal function, previous therapy-induced myelosuppression, or major coexisting illnesses to receive rituximab and either idelalisib (at a dose of 150 mg) or placebo twice daily. The primary end point was progression-free survival. At the first prespecified interim analysis, the study was stopped early on the recommendation of the data and safety monitoring board owing to overwhelming efficacy.
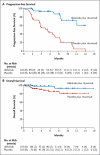
Results: The median progression-free survival was 5.5 months in the placebo group and was not reached in the idelalisib group (hazard ratio for progression or death in the idelalisib group, 0.15; P<0.001). Patients receiving idelalisib versus those receiving placebo had improved rates of overall response (81% vs. 13%; odds ratio, 29.92; P<0.001) and overall survival at 12 months (92% vs. 80%; hazard ratio for death, 0.28; P=0.02). Serious adverse events occurred in 40% of the patients receiving idelalisib and rituximab and in 35% of those receiving placebo and rituximab.
Conclusions: The combination of idelalisib and rituximab, as compared with placebo and rituximab, significantly improved progression-free survival, response rate, and overall survival among patients with relapsed CLL who were less able to undergo chemotherapy. (Funded by Gilead; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01539512.).
Figures


Comment in
-
Idelalisib--a PI3Kδ inhibitor for B-cell cancers.N Engl J Med. 2014 Mar 13;370(11):1061-2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1400055. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 24620870 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Eichhorst B, Goede V, Hallek M. Treatment of elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50:171–8. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, version 2. 2013 ( http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nhl.pdf)
-
- Itälä M, Geisler CH, Kimby E, et al. Standard-dose anti-CD20 antibody rituximab has efficacy in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: results from a Nordic multi-centre study. Eur J Haematol. 2002;69:129–34. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien SM, Kantarjian H, Thomas DA, et al. Rituximab dose-escalation trial in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2165–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
