Exercise-induced skeletal muscle remodeling and metabolic adaptation: redox signaling and role of autophagy
- PMID: 24450966
- PMCID: PMC4048572
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2013.5773
Exercise-induced skeletal muscle remodeling and metabolic adaptation: redox signaling and role of autophagy
Abstract
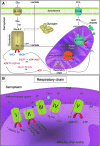
Significance: Skeletal muscle is a highly plastic tissue. Exercise evokes signaling pathways that strongly modify myofiber metabolism and physiological and contractile properties of skeletal muscle. Regular physical activity is beneficial for health and is highly recommended for the prevention of several chronic conditions. In this review, we have focused our attention on the pathways that are known to mediate physical training-induced plasticity.
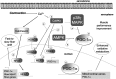
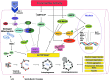
Recent advances: An important role for redox signaling has recently been proposed in exercise-mediated muscle remodeling and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) activation. Still more currently, autophagy has also been found to be involved in metabolic adaptation to exercise.
Critical issues: Both redox signaling and autophagy are processes with ambivalent effects; they can be detrimental and beneficial, depending on their delicate balance. As such, understanding their role in the chain of events induced by exercise and leading to skeletal muscle remodeling is a very complicated matter. Moreover, the study of the signaling induced by exercise is made even more difficult by the fact that exercise can be performed with several different modalities, with this having different repercussions on adaptation.
Future directions: Unraveling the complexity of the molecular signaling triggered by exercise on skeletal muscle is crucial in order to define the therapeutic potentiality of physical training and to identify new pharmacological compounds that are able to reproduce some beneficial effects of exercise. In evaluating the effect of new "exercise mimetics," it will also be necessary to take into account the involvement of reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, and autophagy and their controversial effects.
Figures





References
-
- Abruzzo PM, Esposito F, Marchionni C, di Tullio S, Belia S, Fulle S, Veicsteinas A, and Marini M. Moderate exercise training induces ROS-related adaptations to skeletal muscles. Int J Sports Med 34: 676–687, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Akimoto T, Pohnert SC, Li P, Zhang M, Gumbs C, Rosenberg PB, Williams RS, and Yan Z. Exercise stimulates Pgc-1alpha transcription in skeletal muscle through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem 280: 19587–19593, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Arico S, Petiot A, Bauvy C, Dubbelhuis PF, Meijer AJ, Codogno P, and Ogier-Denis E. The tumor suppressor PTEN positively regulates macroautophagy by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway. J Biol Chem 276: 35243–35246, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Atherton PJ, Babraj J, Smith K, Singh J, Rennie MJ, and Wackerhage H. Selective activation of AMPK-PGC-1alpha or PKB-TSC2-mTOR signaling can explain specific adaptive responses to endurance or resistance training-like electrical muscle stimulation. FASEB J 19: 786–788, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Baar K, Wende AR, Jones TE, Marison M, Nolte LA, Chen M, Kelly DP, and Holloszy JO. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to exercise: rapid increase in the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. FASEB J 16: 1879–1886, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

