Molecular dynamics simulation of the crystallizable fragment of IgG1-insights for the design of Fcabs
- PMID: 24451126
- PMCID: PMC3907818
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15010438
Molecular dynamics simulation of the crystallizable fragment of IgG1-insights for the design of Fcabs
Abstract
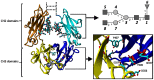
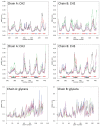
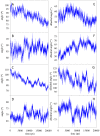
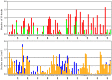
An interesting format in the development of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies uses the crystallizable fragment of IgG1 as starting scaffold. Engineering of its structural loops allows generation of an antigen binding site. However, this might impair the molecule's conformational stability, which can be overcome by introducing stabilizing point mutations in the CH3 domains. These point mutations often affect the stability and unfolding behavior of both the CH2 and CH3 domains. In order to understand this cross-talk, molecular dynamics simulations of the domains of the Fc fragment of human IgG1 are reported. The structure of human IgG1-Fc obtained from X-ray crystallography is used as a starting point for simulations of the wild-type protein at two different pH values. The stabilizing effect of a single point mutation in the CH3 domain as well as the impact of the hinge region and the glycan tree structure connected to the CH2 domains is investigated. Regions of high local flexibility were identified as potential sites for engineering antigen binding sites. Obtained data are discussed with respect to the available X-ray structure of IgG1-Fc, directed evolution approaches that screen for stability and use of the scaffold IgG1-Fc in the design of antigen binding Fc proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Creating stable stem regions for loop elongation in Fcabs - insights from combining yeast surface display, in silico loop reconstruction and molecular dynamics simulations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1844(9):1530-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.04.020. Epub 2014 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24792385 Free PMC article.
-
IgG2 Fc structure and the dynamic features of the IgG CH2-CH3 interface.Mol Immunol. 2013 Nov;56(1-2):131-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.03.018. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23628091
-
Stabilisation of the Fc fragment of human IgG1 by engineered intradomain disulfide bonds.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030083. Epub 2012 Jan 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22272277 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered IgG1-Fc--one fragment to bind them all.Immunol Rev. 2016 Mar;270(1):113-31. doi: 10.1111/imr.12385. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26864108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural analysis of Fc/FcγR complexes: a blueprint for antibody design.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):201-21. doi: 10.1111/imr.12365. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497522 Review.
Cited by
-
Designing antibody against highly conserved region of dengue envelope protein by in silico screening of scFv mutant library.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 10;14(1):e0209576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209576. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30629625 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of complex N-glycans in IgG Fc-region is affected by core fucosylation.MAbs. 2015;7(5):863-70. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1053683. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 26067753 Free PMC article.
-
Thinking outside the Laboratory: Analyses of Antibody Structure and Dynamics within Different Solvent Environments in Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations.Antibodies (Basel). 2018 Jun 24;7(3):21. doi: 10.3390/antib7030021. Antibodies (Basel). 2018. PMID: 31544873 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of glycans and hinge on dynamics in the IgG1 Fc.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024;42(22):12571-12579. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2270749. Epub 2023 Oct 28. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37897185 Free PMC article.
-
Creating stable stem regions for loop elongation in Fcabs - insights from combining yeast surface display, in silico loop reconstruction and molecular dynamics simulations.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1844(9):1530-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.04.020. Epub 2014 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24792385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strebhardt K., Ullrich A. Paul Ehrlich’s magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2008;8:473–480. - PubMed
-
- Ehrlich P. Beiträge zur Experimentellen Pathologie und Chemotherapie. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft; Leipzig, Germany: 1909. Über Den Jetzigen Stand Der Karzinomforschung (in Germany) pp. 117–164.
-
- Kohler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975;256:495–497. - PubMed
-
- Teillaud J. From Whole Monoclonal Antibodies to Single Domain Antibodies: Think Small. In: Saerens D., Muyldermans S., editors. Single Domain Antibodies. Vol. 911. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ, USA: 2012. pp. 3–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

