Hyaluromycin, a new hyaluronidase inhibitor of polyketide origin from marine Streptomyces sp
- PMID: 24451191
- PMCID: PMC3917283
- DOI: 10.3390/md12010491
Hyaluromycin, a new hyaluronidase inhibitor of polyketide origin from marine Streptomyces sp
Abstract
Hyaluromycin (1), a new member of the rubromycin family of antibiotics, was isolated from the culture extract of a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. as a HAase inhibitor on the basis of HAase activity screening. The structure of 1 was elucidated through the interpretation of NMR data for the compound and its 3″-O-methyl derivative in combination with an incorporation experiment with [1,2-13C2]acetate. The compound's absolute configuration was determined by the comparison of its circular dichroism (CD) spectrum with those of other rubromycins. Hyaluromycin (1) consists of a γ-rubromycin core structure possessing a 2-amino-3-hydroxycyclopent-2-enone (C5N) unit as an amide substituent of the carboxyl function; both structural units have been reported only from actinomycetes. Hyaluromycin (1) displayed approximately 25-fold more potent hyaluronidase inhibitory activity against hyaluronidase than did glycyrrhizin, a known inhibitor of plant origin.
Figures

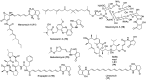
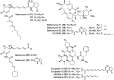







References
-
- Hamai A., Morikawa K., Horei K., Tokuyasu K. Purification and characterization of hyaluronidase from Streptococcus dysgalactiae. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989;53:2163–2168. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.53.2163. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

