Whipple made simple for surgical pathologists: orientation, dissection, and sampling of pancreaticoduodenectomy specimens for a more practical and accurate evaluation of pancreatic, distal common bile duct, and ampullary tumors
- PMID: 24451278
- PMCID: PMC4051141
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000165
Whipple made simple for surgical pathologists: orientation, dissection, and sampling of pancreaticoduodenectomy specimens for a more practical and accurate evaluation of pancreatic, distal common bile duct, and ampullary tumors
Abstract
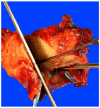
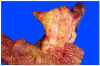
Pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) specimens present a challenge for surgical pathologists because of the relative rarity of these specimens, combined with the anatomic complexity. Here, we describe our experience on the orientation, dissection, and sampling of PD specimens for a more practical and accurate evaluation of pancreatic, distal common bile duct (CBD), and ampullary tumors. For orientation of PDs, identification of the "trapezoid," created by the vascular bed at the center, the pancreatic neck margin on the left, and the uncinate margin on the right, is of outmost importance in finding all the pertinent margins of the specimen including the CBD, which is located at the upper right edge of this trapezoid. After orientation, all the margins can be sampled. We submit the uncinate margin entirely as a perpendicular inked margin because this adipose tissue-rich area often reveals subtle satellite carcinomas that are grossly invisible, and, with this approach, the number of R1 resections has doubled in our experience. Then, to ensure proper identification of all lymph nodes (LNs), we utilize the orange-peeling approach, in which the soft tissue surrounding the pancreatic head is shaved off in 7 arbitrarily defined regions, which also serve as shaved samples of the so-called "peripancreatic soft tissue" that defines pT3 in the current American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM. With this approach, our LN count increased from 6 to 14 and LN positivity rate from 50% to 73%. In addition, in 90% of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas there are grossly undetected microfoci of carcinoma. For determination of the primary site and the extent of the tumor, we believe bisectioning of the pancreatic head, instead of axial (transverse) slicing, is the most revealing approach. In addition, documentation of the findings in the duodenal surface of the ampulla is crucial for ampullary carcinomas and their recent site-specific categorization into 4 categories. Therefore, we probe both the CBD and the pancreatic duct from distal to the ampulla and cut the pancreatic head to the ampulla at a plane that goes through both ducts. Then, we sample the bisected pancreatic head depending on the findings of the case. For example, for proper staging of ampullary carcinomas, it is imperative to take the sections perpendicular to the duodenal serosa at the "groove" area, as ampullary carcinomas often extend to this region. Amputative (axial) sectioning of the ampulla, although good for documentation of the peri-Oddi spread of the intra-ampullary tumors, unfortunately disallows documentation of mucosal spread of the papilla of Vater tumors (those arising from the edge of the ampulla, where the ducts transition to duodenal mucosa and extending) into the neighboring duodenum. Axial sectioning also often fails to document tumor spread to the "groove" area. In conclusion, knowledge of the gross characteristics of the anatomic hallmarks is essential for proper dissection of PD specimens. The approach described above allows practical and accurate documentation and staging of pancreas, distal CBD, and ampullary cancers.
Figures










References
-
- Birkmeyer JD, Siewers AE, Finlayson EV, et al. Hospital volume and surgical mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1128–1137. - PubMed
-
- Bruzoni M, Johnston E, Sasson AR. Pancreatic incidentalomas: clinical and pathologic spectrum. Am J Surg. 2008;195:329–332. discussion 332. - PubMed
-
- Hopt U, Keck T. Pancreatic incidentalomas. Correct assessment and therapy. Chirurg. 2007;78:713–720. - PubMed
-
- Basturk O, Coban I, Adsay NV. Pancreatic cysts: pathologic classification, differential diagnosis, and clinical implications. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:423–438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

