Serodiagnosis of equine leptospirosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using four recombinant protein markers
- PMID: 24451330
- PMCID: PMC3993115
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00649-13
Serodiagnosis of equine leptospirosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using four recombinant protein markers
Abstract
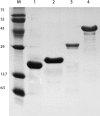
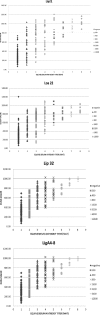
Leptospirosis, caused by Leptospira spp., is one of the most common zoonotic diseases in the world. We tested four recombinant proteins of Leptospira interrogans, namely, rLipL21, rLoa22, rLipL32, and rLigACon4-8, to evaluate their potential for use as antigens for the diagnosis of equine leptospirosis. We employed equine sera (n = 130) that were microscopic agglutination test (MAT) negative and sera (n = 176) that were MAT positive for the 5 serovars that most commonly cause equine leptospirosis. The sensitivity and specificity of ELISA compared to MAT were 82.39% and 86.15%, respectively, for LigACon4-8, 77.84% and 92.31%, respectively, for Loa22, 77.84% and 86.15%, respectively, for LipL32, and 84.66% and 83.85%, respectively, for LipL21. When one of the two antigens was test positive, the sensitivity and specificity of ELISA were 93.75% and 78.46%, respectively, for rLigACon4-8 and LipL32, 93.18% and 76.15%, respectively, for rLigACon4-8 and LipL21, 89.77% and 80.77%, respectively, for rLigACon4-8 and Loa22, 91.48% and 78.46%, respectively, for LipL21 and Loa22, 93.75% and 76.92%, respectively, for LipL21 and LipL32, and 90.34% and 80.77%, respectively, for Loa22 and LipL32. In conclusion, we have developed an indirect ELISA utilizing rLigACon4-8, rLoa22, rLipL32, and rLipL21 as diagnostic antigens for equine leptospirosis. The use of four antigens in the ELISA was found to be sensitive and specific, the assay was easy to perform, and the results concurred with the results of the standard Leptospira MAT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recombinant antigens rLipL21, rLoa22, rLipL32 and rLigACon4-8 for serological diagnosis of leptospirosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in dogs.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 19;9(12):e111367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111367. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25526513 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment and application of ELISAs based on rLipL32/1-LipL21-OmpL1/2 fusion antigen of Leptospira interrogans].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008 Nov;37(6):592-8. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2008.06.009. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008. PMID: 19084957 Chinese.
-
Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a recombinant LigA fragment comprising repeat domains 4 to 7.5 as an antigen for diagnosis of equine leptospirosis.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013 Aug;20(8):1143-9. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00245-13. Epub 2013 May 29. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23720368 Free PMC article.
-
Equine genital leptospirosis: Evidence of an important silent chronic reproductive syndrome.Theriogenology. 2022 Oct 15;192:81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.08.029. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Theriogenology. 2022. PMID: 36063673 Review.
-
Insight into the Structure, Functions, and Dynamics of the Leptospira Outer Membrane Proteins with the Pathogenicity.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Mar 7;12(3):300. doi: 10.3390/membranes12030300. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35323775 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of anti-Leptospira antibodies by microscopic agglutination test in ruminants and equines of Urmia, Iran.Vet Res Forum. 2023;14(4):229-235. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2022.546475.3345. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Vet Res Forum. 2023. PMID: 37181853 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospiral Immunoglobulin-Like Domain Proteins: Roles in Virulence and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 8;11:579907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.579907. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33488581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant antigens rLipL21, rLoa22, rLipL32 and rLigACon4-8 for serological diagnosis of leptospirosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in dogs.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 19;9(12):e111367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111367. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25526513 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence, frequency of leptospiuria, and associated risk factors in horses in Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska from 2016-2017.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 29;13(10):e0206639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206639. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30372498 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immunodominant antigens in canine leptospirosis by Multi-Antigen Print ImmunoAssay (MAPIA).BMC Vet Res. 2014 Dec 3;10:288. doi: 10.1186/s12917-014-0288-2. BMC Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 25466383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faisal SM, McDonough SP, Chang YF. 2012. Leptospira: invasion, pathogenesis and persistence, p 143–172 In Embers ME. (ed), The pathogenic spirochetes: strategies for evasion of host immunity and persistence. Springer Science, New York, NY
-
- Divers TJ, Byars TD, Shin SJ. 1992. Renal dysfunction associated with infection of Leptospira interrogans in a horse. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 201:1391–1392 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

