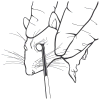
Safety and blood sample volume and quality of a refined retro-orbital bleeding technique in rats using a lateral approach
- PMID: 24451361
- PMCID: PMC3989930
- DOI: 10.1038/laban.432
Safety and blood sample volume and quality of a refined retro-orbital bleeding technique in rats using a lateral approach
Abstract
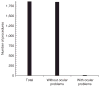
The collection of blood samples from laboratory rats requires the use of bleeding techniques that provide quality samples of sufficient volume for analysis without injury to the animal. Retro-orbital bleeding (ROB) is a phlebotomy technique that can yield high-quality samples of adequate volume, but it has been criticized for its potential to cause injury. To evaluate the injury-causing potential of their refined ROB method using a lateral approach, the authors retrospectively reviewed ROB procedures carried out in their colony during an 18-month period and found that 0.6% of these procedures were associated with ocular injury. The authors also compared the quality of blood samples collected by ROB and by saphenous phlebotomy and found that ROB yielded samples of better quality. The authors conclude that, when done using a lateral approach and by an experienced technician, ROB is humane and safe and provides blood samples of adequate volume and quality for analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Orbital sinus blood sampling in rats as performed by different animal technicians: the influence of technique and expertise.Lab Anim. 1998 Oct;32(4):377-86. doi: 10.1258/002367798780599794. Lab Anim. 1998. PMID: 9807751
-
Pharmacokinetic comparisons of tail-bleeding with cannula- or retro-orbital bleeding techniques in rats using six marketed drugs.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2007 Sep-Oct;56(2):256-64. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2007.05.006. Epub 2007 Jun 2. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2007. PMID: 17618130
-
Subclavian Vein Puncture As an Alternative Method of Blood Sample Collection in Rats.J Vis Exp. 2018 Nov 18;(141). doi: 10.3791/58499. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30507916
-
[Joint EFLM-COLABIOCLI recommendation for venous blood sampling].Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2019 Apr 1;77(2):131-154. doi: 10.1684/abc.2019.1419. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 2019. PMID: 30998194 Review. French.
-
Less is better: why venepuncture practice should be reviewed for those with end-stage renal failure.Prof Nurse. 2003 Feb;18(6):344-6. Prof Nurse. 2003. PMID: 12630247 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Hydration and Antibiotics with Lisinopril to Mitigate Acute and Delayed High-dose Radiation Injuries to Multiple Organs.Health Phys. 2016 Nov;111(5):410-9. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000554. Health Phys. 2016. PMID: 27682899 Free PMC article.
-
AT 1 inhibition mediated neuroprotection after experimental traumatic brain injury is dependent on neutrophils in male mice.Sci Rep. 2023 May 7;13(1):7413. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33797-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37150755 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Treatment with Plant-Derived Exosomes Restores Redox Balance in H2O2-Treated Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 29;12(6):1169. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061169. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371899 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo longitudinal 920 nm two-photon intravital kidney imaging of a dynamic 2,8-DHA crystal formation and tubular deterioration in the adenine-induced chronic kidney disease mouse model.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Mar 27;14(4):1647-1658. doi: 10.1364/BOE.485187. eCollection 2023 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 37078028 Free PMC article.
-
Renal involvement in the pathogenesis of mineral and bone disorder in dystrophin-deficient mdx mouse.J Physiol Sci. 2019 Jul;69(4):661-671. doi: 10.1007/s12576-019-00683-8. Epub 2019 May 11. J Physiol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31079351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diehl KH, et al. A good practice guide to the administration of substances and removal of blood, including routes and volumes. J Appl Toxicol. 2001;21:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Frank JJ, Bermes EW, Bickel MJ, Watkins BF. Effect of in vitro hemolysis on chemical values for serum. Clin Chem. 1978;24:1966–1970. - PubMed
-
- Stender RN, Engler WJ, Braun TM, Hankenson FC. Establishment of blood analyte intervals for laboratory mice and rats by use of a portable clinical analyzer. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2007;46:47–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources