p53 protein regulates Hsp90 ATPase activity and thereby Wnt signaling by modulating Aha1 expression
- PMID: 24451373
- PMCID: PMC3945316
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.532523
p53 protein regulates Hsp90 ATPase activity and thereby Wnt signaling by modulating Aha1 expression
Retraction in
-
Withdrawal: p53 protein regulates Hsp90 ATPase activity and thereby Wnt signaling by modulating Aha1 expression.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jan 3;295(1):289. doi: 10.1074/jbc.W119.012134. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31900371 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
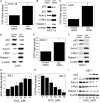
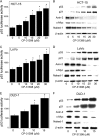
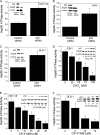
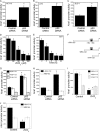
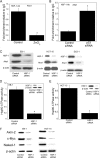
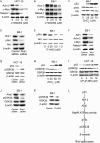
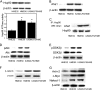
The p53 tumor suppressor gene encodes a homotetrameric transcription factor which is activated in response to a variety of cellular stressors, including DNA damage and oncogene activation. p53 mutations occur in >50% of human cancers. Although p53 has been shown to regulate Wnt signaling, the underlying mechanisms are not well understood. Here we show that silencing p53 in colon cancer cells led to increased expression of Aha1, a co-chaperone of Hsp90. Heat shock factor-1 was important for mediating the changes in Aha1 levels. Increased Aha1 levels were associated with enhanced interactions with Hsp90, resulting in increased Hsp90 ATPase activity. Moreover, increased Hsp90 ATPase activity resulted in increased phosphorylation of Akt and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β), leading to enhanced expression of Wnt target genes. Significantly, levels of Aha1, Hsp90 ATPase activity, Akt, and GSK3β phosphorylation and expression of Wnt target genes were increased in the colons of p53-null as compared with p53 wild type mice. Using p53 heterozygous mutant epithelial cells from Li-Fraumeni syndrome patients, we show that a monoallelic mutation of p53 was sufficient to activate the Aha1/Hsp90 ATPase axis leading to stimulation of Wnt signaling and increased expression of Wnt target genes. Pharmacologic intervention with CP-31398, a p53 rescue agent, inhibited recruitment of Aha1 to Hsp90 and suppressed Wnt-mediated gene expression in colon cancer cells. Taken together, this study provides new insights into the mechanism by which p53 regulates Wnt signaling and raises the intriguing possibility that p53 status may affect the efficacy of anticancer therapies targeting Hsp90 ATPase.
Keywords: Colon Cancer; Hsp90; Wnt Pathway; p53; β-Catenin.
Figures



Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2023 Sep 13;88(176):62800-62803. Fed Regist. 2023. PMID: 37736072 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2023 Sep 13;88(176):62803-62807. Fed Regist. 2023. PMID: 37736073 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Polakis P. (2000) Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 14, 1837–1851 - PubMed
-
- Bienz M., Clevers H. (2000) Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 103, 311–320 - PubMed
-
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. (1996) Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell 87, 159–170 - PubMed
-
- Mikels A. J., Nusse R. (2006) Wnts as ligands: processing, secretion and reception. Oncogene 25, 7461–7468 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

