Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate the transcriptional regulation of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-a gene: interactive roles of modified histones, histone acetyltransferase, p300, AND Sp1
- PMID: 24451378
- PMCID: PMC3945360
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511444
Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate the transcriptional regulation of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-a gene: interactive roles of modified histones, histone acetyltransferase, p300, AND Sp1
Abstract
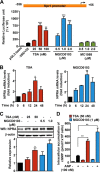
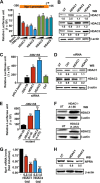
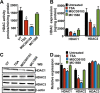
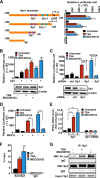
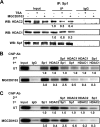
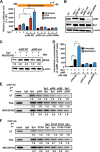
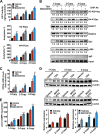
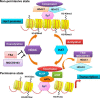
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) binds guanylyl cyclase-A/natriuretic peptide receptor-A (GC-A/NPRA) and produces the intracellular second messenger, cGMP, which regulates cardiovascular homeostasis. We sought to determine the function of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in regulating Npr1 (coding for GC-A/NPRA) gene transcription, using primary mouse mesangial cells treated with class-specific HDAC inhibitors (HDACi). Trichostatin A, a pan inhibitor, and mocetinostat (MGCD0103), a class I HDAC inhibitor, significantly enhanced Npr1 promoter activity (by 8- and 10-fold, respectively), mRNA levels (4- and 5.3-fold, respectively), and NPRA protein (2.7- and 3.5-fold, respectively). However, MC1568 (class II HDAC inhibitor) had no discernible effect. Overexpression of HDAC1 and HDAC2 significantly attenuated Npr1 promoter activity, whereas HDAC3 and HDAC8 had no effect. HDACi-treated cultured cells in vitro and intact animals in vivo showed significantly reduced binding of HDAC1 and -2 and increased accumulation of acetylated H3-K9/14 and H4-K12 at the Npr1 promoter. Deletional analyses of the Npr1 promoter along with ectopic overexpression and inhibition of Sp1 confirmed that HDACi-induced Npr1 gene transcription is accomplished by Sp1 activation. Furthermore, HDACi attenuated the interaction of Sp1 with HDAC1/2 and promoted Sp1 association with p300 and p300/cAMP-binding protein-associated factor; it also promoted the recruitment of p300 and p300/cAMP-binding protein-associated factor to the Npr1 promoter. Our results demonstrate that trichostatin A and MGCD0103 enhanced Npr1 gene expression through inhibition of HDAC1/2 and increased both acetylation of histones (H3-K9/14, H4-K12) and Sp1 by p300, and their recruitment to Npr1 promoter. Our findings define a novel epigenetic regulatory mechanism that governs Npr1 gene transcription.
Keywords: Chromatin Histone Modification; Gene Transcription; Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors; Natriuretic Peptides; Sp1; p300.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interactive roles of Ets-1, Sp1, and acetylated histones in the retinoic acid-dependent activation of guanylyl cyclase/atrial natriuretic peptide receptor-A gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 26;285(48):37521-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.132795. Epub 2010 Sep 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20864529 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans retinoic acid and sodium butyrate enhance natriuretic peptide receptor a gene transcription: role of histone modification.Mol Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;85(6):946-57. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.092221. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Mol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24714214 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-specific expression of aquaporin-5 (Aqp5) in alveolar epithelium is directed by GATA6/Sp1 via histone acetylation.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 14;7(1):3473. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03152-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28615712 Free PMC article.
-
Dual mechanisms of regulation of transcription of luteinizing hormone receptor gene by nuclear orphan receptors and histone deacetylase complexes.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;85(2-5):401-14. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(03)00230-9. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12943729 Review.
-
Epigenetic therapy of cancer with histone deacetylase inhibitors.J Cancer Res Ther. 2014 Jul-Sep;10(3):469-78. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.137937. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25313724 Review.
Cited by
-
Podocyte cell-specific Npr1 is required for blood pressure and renal homeostasis in male and female mice: role of sex-specific differences.Physiol Genomics. 2024 Oct 1;56(10):672-690. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00137.2023. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Physiol Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39101921 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylases Inhibitors in the Treatment of Retinal Degenerative Diseases: Overview and Perspectives.J Ophthalmol. 2015;2015:250812. doi: 10.1155/2015/250812. Epub 2015 Jun 2. J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26137316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal Role Of DNA Methylation And Sp1 Binding In Ki-67 Gene Transcription.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Nov 18;11:9749-9759. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S213769. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31819613 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Epigenetic Mechanisms Regulating Blood Pressure and Kidney Dysfunction.Hypertension. 2024 Jul;81(7):1424-1437. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.22072. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Hypertension. 2024. PMID: 38545780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming growth factor β1 antagonizes the transcription, expression and vascular signaling of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor A - role of δEF1.FEBS J. 2016 May;283(9):1767-81. doi: 10.1111/febs.13701. Epub 2016 Apr 5. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26934489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drewett J. G., Garbers D. L. (1994) The family of guanylyl cyclase receptors and their ligands. Endocr. Rev. 15, 135–162 - PubMed
-
- de Bold A. J. (1985) Atrial natriuretic factor. A hormone produced by the heart. Science 230, 767–770 - PubMed
-
- Pandey K. N., Singh S. (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of murine guanylate cyclase/atrial natriuretic factor receptor cDNA. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 12342–12348 - PubMed
-
- Levin E. R., Gardner D. G., Samson W. K. (1998) Natriuretic peptides. N. Engl. J. Med. 339, 321–328 - PubMed
-
- Pandey K. N. (2005) Biology of natriuretic peptides and their receptors. Peptides 26, 901–932 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

