A redox-resistant sirtuin-1 mutant protects against hepatic metabolic and oxidant stress
- PMID: 24451382
- PMCID: PMC3953247
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.520403
A redox-resistant sirtuin-1 mutant protects against hepatic metabolic and oxidant stress
Abstract
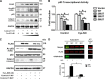
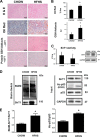
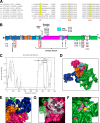
Sirtuin-1 (SirT1), a member of the NAD(+)-dependent class III histone deacetylase family, is inactivated in vitro by oxidation of critical cysteine thiols. In a model of metabolic syndrome, SirT1 activation attenuated apoptosis of hepatocytes and improved liver function including lipid metabolism. We show in SirT1-overexpressing HepG2 cells that oxidants (nitrosocysteine and hydrogen peroxide) or metabolic stress (high palmitate and high glucose) inactivated SirT1 by reversible oxidative post-translational modifications (OPTMs) on three cysteines. Mutating these oxidation-sensitive cysteines to serine preserved SirT1 activity and abolished reversible OPTMs. Overexpressed mutant SirT1 maintained deacetylase activity and attenuated proapoptotic signaling, whereas overexpressed wild type SirT1 was less protective in metabolically or oxidant-stressed cells. To prove that OPTMs of SirT1 are glutathione (GSH) adducts, glutaredoxin-1 was overexpressed to remove this modification. Glutaredoxin-1 overexpression maintained endogenous SirT1 activity and prevented proapoptotic signaling in metabolically stressed HepG2 cells. The in vivo significance of oxidative inactivation of SirT1 was investigated in livers of high fat diet-fed C57/B6J mice. SirT1 deacetylase activity was decreased in the absence of changes in SirT1 expression and associated with a marked increase in OPTMs. These results indicate that glutathione adducts on specific SirT1 thiols may be responsible for dysfunctional SirT1 associated with liver disease in metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: Glutathiolation; Glutathionylation; High Fat High Sucrose Diet; Metabolic Diseases; Oxidative Stress; Polyphenols; Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species; Resveratrol.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Oxidized GAPDH transfers S-glutathionylation to a nuclear protein Sirtuin-1 leading to apoptosis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Oct;174:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.037. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34332079 Free PMC article.
-
Glutaredoxin-1 Deficiency Causes Fatty Liver and Dyslipidemia by Inhibiting Sirtuin-1.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Aug 20;27(6):313-327. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6716. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27958883 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 is a redox-sensitive deacetylase that is post-translationally modified by oxidants and carbonyl stress.FASEB J. 2010 Sep;24(9):3145-59. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-151308. Epub 2010 Apr 12. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20385619 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Regulation via Glutaredoxin-1 and Protein S-Glutathionylation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 Apr 1;32(10):677-700. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7963. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020. PMID: 31813265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Glutaredoxin-1 and Glutathionylation in Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 16;21(18):6803. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186803. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32948023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sperm cryopreservation and DNA methylation: possible implications for ART success and the health of offspring.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022 Aug;39(8):1815-1824. doi: 10.1007/s10815-022-02545-6. Epub 2022 Jun 17. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022. PMID: 35713751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved mass spectrometry-based activity assay reveals oxidative and metabolic stress as sirtuin-1 regulators.Redox Biol. 2019 Apr;22:101150. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101150. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30877853 Free PMC article.
-
Causes and Consequences of Age-Related Changes in DNA Methylation: A Role for ROS?Biology (Basel). 2014 Jun 18;3(2):403-25. doi: 10.3390/biology3020403. Biology (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24945102 Free PMC article.
-
Overnutrition Determines LPS Regulation of Mycotoxin Induced Neurotoxicity in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Dec 10;16(12):29554-73. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226190. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26690419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol Binge Drinking Selectively Stimulates Protein S-Glutathionylation in Aorta and Liver of ApoE -/- Mice.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 16;8:649813. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.649813. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33796575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ribeiro P. S., Cortez-Pinto H., Solá S., Castro R. E., Ramalho R. M., Baptista A., Moura M. C., Camilo M. E., Rodrigues C. M. (2004) Hepatocyte apoptosis, expression of death receptors, and activation of NF-κB in the liver of nonalcoholic and alcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 99, 1708–1717 - PubMed
-
- Elliott P. J., Jirousek M. (2008) Sirtuins: novel targets for metabolic disease. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 9, 371–378 - PubMed
-
- Westphal C. H., Dipp M. A., Guarente L. (2007) A therapeutic role for sirtuins in diseases of aging? Trends Biochem. Sci. 32, 555–560 - PubMed
-
- Potente M., Dimmeler S. (2008) Emerging roles of SIRT1 in vascular endothelial homeostasis. Cell Cycle 7, 2117–2122 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

