Transcriptome-wide investigation of genomic imprinting in chicken
- PMID: 24452801
- PMCID: PMC3973300
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1390
Transcriptome-wide investigation of genomic imprinting in chicken
Abstract
Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic mechanism by which alleles of some specific genes are expressed in a parent-of-origin manner. It has been observed in mammals and marsupials, but not in birds. Until now, only a few genes orthologous to mammalian imprinted ones have been analyzed in chicken and did not demonstrate any evidence of imprinting in this species. However, several published observations such as imprinted-like QTL in poultry or reciprocal effects keep the question open. Our main objective was thus to screen the entire chicken genome for parental-allele-specific differential expression on whole embryonic transcriptomes, using high-throughput sequencing. To identify the parental origin of each observed haplotype, two chicken experimental populations were used, as inbred and as genetically distant as possible. Two families were produced from two reciprocal crosses. Transcripts from 20 embryos were sequenced using NGS technology, producing ∼200 Gb of sequences. This allowed the detection of 79 potentially imprinted SNPs, through an analysis method that we validated by detecting imprinting from mouse data already published. However, out of 23 candidates tested by pyrosequencing, none could be confirmed. These results come together, without a priori, with previous statements and phylogenetic considerations assessing the absence of genomic imprinting in chicken.
Figures

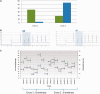
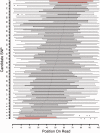
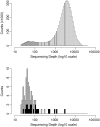
References
-
- da Rocha ST, Ferguson-Smith AC. Genomic imprinting. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:R646–R649. - PubMed
-
- Holman L, Kokko H. The evolution of genomic imprinting: costs, benefits and long-term consequences. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2013 (doi: 10.1111/brv.12069; epub ahead of print, October 28, 2013) - PubMed
-
- Haig D, Graham C. Genomic imprinting and the strange case of the insulin-like growth factor II receptor. Cell. 1991;64:1045–1046. - PubMed
-
- Moore T, Haig D. Genomic imprinting in mammalian development: a parental tug-of-war. Trends Genet. 1991;7:45–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

