Stepwise assembly of multiple Lin28 proteins on the terminal loop of let-7 miRNA precursors
- PMID: 24452802
- PMCID: PMC3985620
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1391
Stepwise assembly of multiple Lin28 proteins on the terminal loop of let-7 miRNA precursors
Abstract
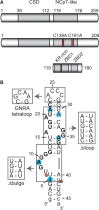
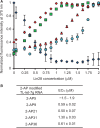
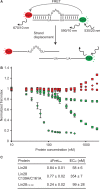
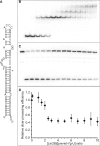
Lin28 inhibits the biogenesis of let-7 miRNAs through direct interactions with let-7 precursors. Previous studies have described seemingly inconsistent Lin28 binding sites on pre-let-7 RNAs. Here, we reconcile these data by examining the binding mechanism of Lin28 to the terminal loop of pre-let-7g (TL-let-7g) using biochemical and biophysical methods. First, we investigate Lin28 binding to TL-let-7g variants and short RNA fragments and identify three independent binding sites for Lin28 on TL-let-7g. We then determine that Lin28 assembles in a stepwise manner on TL-let-7g to form a stable 1:3 complex. We show that the cold-shock domain (CSD) of Lin28 is responsible for remodelling the terminal loop of TL-let-7g, whereas the NCp7-like domain facilitates the initial binding of Lin28 to TL-let-7g. This stable binding of multiple Lin28 molecules to the terminal loop of pre-let-7g extends to other precursors of the let-7 family, but not to other pre-miRNAs tested. We propose a model for stepwise assembly of the 1:1, 1:2 and 1:3 pre-let-7g/Lin28 complexes. Stepwise multimerization of Lin28 on pre-let-7 is required for maximum inhibition of Dicer cleavage for a least one member of the let-7 family and may be important for orchestrating the activity of the several factors that regulate let-7 biogenesis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

