Contribution of protein kinase Cα in the stimulation of insulin by the down-regulation of Cavβ subunits
- PMID: 24452871
- PMCID: PMC4176602
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-013-0149-y
Contribution of protein kinase Cα in the stimulation of insulin by the down-regulation of Cavβ subunits
Abstract
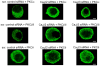
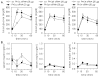
Voltage-gated calcium (Cav) channels and protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes are involved in insulin secretion. In addition, Cavβ, one of the auxiliary subunits of Cav channels, also regulates the secretion of insulin as knockout of Cavβ3 (β3(-/-)) subunits in mice led to efficient glucose homeostasis and increased insulin levels. We examined whether other types of Cavβ subunits also have similar properties. In this regard, we used small interfering RNA (siRNA) of these subunits (20 μg each) to down-regulate them and examined blood glucose, serum insulin and PKC translocation in isolated pancreatic β cells of mice. While the down-regulation of Cavβ2 and β3 subunits increased serum insulin levels and caused efficient glucose homeostasis, the down-regulation of Cavβ1 and β4 subunits failed to affect both these parameters. Examination of PKC isozymes in the pancreatic β-cells of Cavβ2- or β3 siRNA-injected mice showed that three PKC isozymes, viz., PKC α, βII and θ, translocated to the membrane. This suggests that when present, Cavβ2 and β3 subunits inhibited PKC activation. Among these three isozymes, only PKCα siRNA inhibited insulin and increased glucose concentrations. It is possible that the activation of PKCs βII and θ is not sufficient for the release of insulin and PKCα is the mediator of insulin secretion under the control of Cavβ subunits. Since Cavβ subunits are present intracellularly, it is possible that they (1) inhibited the translocation of PKC isozymes to the membrane and (2) decreased the interaction between Cav channels and PKC isozymes and thus the secretion of insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors fully declare any financial or other potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54:87–143. - PubMed
-
- Straub S, Sharp G. Glucose-stimulated signaling pathways in biphasic insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Res. 2002;18:451–463. - PubMed
-
- Yang S, Berggren PO. β-cell Cav channel regulation in physiology and pathophysiology. Am J Physiol-Endoc M. 2005;288:E16–E28. - PubMed
-
- Yedovitzky M, Mochly-Rosen D, Johnson J, Gray M, Ron D, Abramovitch E, Cerasi E, Nesher R. Translocation inhibitors define specificity of protein kinase C isozymes in pancreatic β-cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:1417–1420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

