APOE ε4 worsens hippocampal CA1 apical neuropil atrophy and episodic memory
- PMID: 24453080
- PMCID: PMC3945665
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000154
APOE ε4 worsens hippocampal CA1 apical neuropil atrophy and episodic memory
Abstract
Objectives: Using high-resolution structural MRI, we endeavored to study the relationships among APOE ε4, hippocampal subfield and stratal anatomy, and episodic memory.
Methods: Using a cross-sectional design, we studied 11 patients with Alzheimer disease dementia, 14 patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment, and 14 age-matched healthy controls with no group differences in APOE ε4 carrier status. Each subject underwent ultra-high-field 7.0-tesla MRI targeted to the hippocampus and neuropsychological assessment.
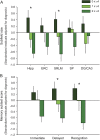
Results: We found a selective, dose-dependent association of APOE ε4 with greater thinning of the CA1 apical neuropil, or stratum radiatum/stratum lacunosum-moleculare (CA1-SRLM), a hippocampal subregion known to exhibit early vulnerability to neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer disease. The relationship between the ε4 allele and CA1-SRLM thinning persisted after controlling for dementia severity, and the size of other hippocampal subfields and the entorhinal cortex did not differ by APOE ε4 carrier status. Carriers also exhibited worse episodic memory function but similar performance in other cognitive domains compared with noncarriers. In a statistical mediation analysis, we found support for the hypothesis that CA1-SRLM thinning may link the APOE ε4 allele to its phenotypic effects on memory.
Conclusions: The APOE ε4 allele segregated dose-dependently and selectively with CA1-SRLM thinning and worse episodic memory performance in a pool of older subjects across a cognitive spectrum. These findings highlight a possible role for this gene in influencing a critical hippocampal subregion and an associated symptomatic manifestation.
Figures
References
-
- Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1993;43:1467–1472 - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 1993;261:921–923 - PubMed
-
- Lehtovirta M, Laakso MP, Soininen H, et al. Volumes of hippocampus, amygdala and frontal lobe in Alzheimer patients with different apolipoprotein E genotypes. Neuroscience 1995;67:65–72 - PubMed
-
- Geroldi C, Pihlajamäki M, Laakso MP, et al. APOE-ε4 is associated with less frontal and more medial temporal lobe atrophy in AD. Neurology 1999;53:1825–1832 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
