TMJ degeneration in SAMP8 mice is accompanied by deranged Ihh signaling
- PMID: 24453178
- PMCID: PMC3929979
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034513519649
TMJ degeneration in SAMP8 mice is accompanied by deranged Ihh signaling
Abstract
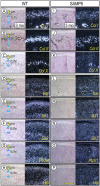
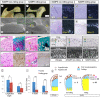
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) functions as a load-bearing diarthrodial joint during mastication, and its continuous use and stress can lead to degeneration over age. Using senescence-accelerated (SAMP8) mice that develop early osteoarthritis-like changes in synovial joints at high frequency, we analyzed possible molecular mechanisms of TMJ degeneration and tested whether and how malocclusion may accelerate it. Condylar articular cartilage in young SAMP8 mice displayed early-onset osteoarthritic changes that included reductions in superficial/chondroprogenitor cell number, proteoglycan/collagen content, and Indian hedgehog (Ihh)-expressing chondrocytes. Following malocclusion induced by tooth milling, the SAMP8 condyles became morphologically defective, displayed even lower proteoglycan levels, and underwent abnormal chondrocyte maturation compared with malocclusion-treated condyles in wild-type mice. Malocclusion also induced faster progression of pathologic changes with increasing age in SAMP8 condyles as indicated by decreased PCNA-positive proliferating chondroprogenitors and increased TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells. These changes were accompanied by steeper reductions in Ihh signaling and by expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 at the chondro-osseous junction in SAMP8 articular cartilage. In sum, we show for the first time that precocious TMJ degeneration in SAMP8 mice is accompanied by--and possibly attributable to--altered Ihh signaling and that occlusal dysfunction accelerates progression toward degenerative TMJ disease in this model.
Keywords: Indian hedgehog; degenerative joint disease; osteoarthritis; senescence-accelerated mouse; superficial cell; temporomandibular joint.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Osteophyte formation and matrix mineralization in a TMJ osteoarthritis mouse model are associated with ectopic hedgehog signaling.Matrix Biol. 2016 May-Jul;52-54:339-354. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Matrix Biol. 2016. PMID: 26945615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Indian Hedgehog Signaling in TMJ Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 13;20(24):6300. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246300. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31847127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lubricin is Required for the Structural Integrity and Post-natal Maintenance of TMJ.J Dent Res. 2014 Jul;93(7):663-70. doi: 10.1177/0022034514535807. Epub 2014 May 16. J Dent Res. 2014. PMID: 24834922 Free PMC article.
-
Ectodysplasin-A deficiency exacerbates TMJOA by upregulating ATF4/Ihh signaling in mice.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025 Aug;33(8):965-979. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2025.02.789. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025. PMID: 40139647
-
Hedgehog signal expression in articular cartilage of rat temporomandibular joint and association with adjuvant-induced osteoarthritis.J Oral Pathol Med. 2017 Apr;46(4):284-291. doi: 10.1111/jop.12497. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Oral Pathol Med. 2017. PMID: 27646982
Cited by
-
Osteophyte formation and matrix mineralization in a TMJ osteoarthritis mouse model are associated with ectopic hedgehog signaling.Matrix Biol. 2016 May-Jul;52-54:339-354. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Matrix Biol. 2016. PMID: 26945615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photobiostimulation conjugated with stem cells or their secretome for temporomandibular joint arthritis in a rat model.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Oct 5;23(1):720. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03466-1. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37798702 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Mutations Associated with Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: A Systematic Review.OAlib. 2015 Jun;2(6):e1583. doi: 10.4236/oalib.1101583. Epub 2015 Jun 3. OAlib. 2015. PMID: 27695703 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Indian Hedgehog Signaling in TMJ Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 13;20(24):6300. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246300. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31847127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A loss of primary cilia by a reduction in mTOR signaling correlates with age-related deteriorations in condylar cartilage.Geroscience. 2024 Dec;46(6):5995-6007. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01143-x. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 38526843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouvier M. (1988). Effects of age on the ability of the rat temporomandibular joint to respond to changing functional demands. J Dent Res 67:1206-1212. - PubMed
-
- Corbit KC, Aanstad P, Singla V, Norman AR, Stainier DY, Reiter JF. (2005). Vertebrate Smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature 437:1018-1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

