Modeling Disease Progression with Longitudinal Markers
- PMID: 24453387
- PMCID: PMC3896511
- DOI: 10.1198/016214507000000356
Modeling Disease Progression with Longitudinal Markers
Abstract
In this paper we propose a Bayesian natural history model for disease progression based on the joint modeling of longitudinal biomarker levels, age at clinical detection of disease and disease status at diagnosis. We establish a link between the longitudinal responses and the natural history of the disease by using an underlying latent disease process which describes the onset of the disease and models the transition to an advanced stage of the disease as dependent on the biomarker levels. We apply our model to the data from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging on prostate specific antigen (PSA) to investigate the natural history of prostate cancer.
Keywords: Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods; Natural history model; disease progression; latent variables; longitudinal response; prostate specific antigen.
Figures
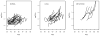


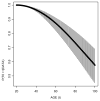
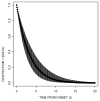
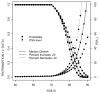
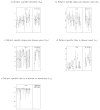

References
-
- Bartoszynski R, Edler L, Hanin L, Kopp-Schneider A, Pavlova L, Tsodikov A, Zorin A, Yakovlev AY. Modeling cancer detection: tumor size as a source of information on unobservable stages of carcinogenesis. Math Biosci. 2001;171(2):113–42. - PubMed
-
- Brookmeyer R. Reconstruction and future trends of the AIDS epidemic in the United States. Science. 1991;253:37–42. - PubMed
-
- Brookmeyer R, Goedert JJ. Censoring in an epidemic with an application to hemophilia-associated AIDS. Biometrics. 1989;45:325–335. - PubMed
-
- Carter HB, Epstein JI, Chan DW, Fozard JL, Pearson JD. Recommended Prostate-Specific Antigen Testing Intervals for the Detection of Curable Prostate Cancer. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1997;277(18):1456–1460. - PubMed
-
- Craig BA, Fryback DG, Klein R, Klein BEK. A Bayesian approach to modelling the natural history of a chronic condition from observations with intervention. Statistics in Medicine. 1999;18:1355–1371. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
