Significant association between serum interleukin-6 and Helicobacter pylori antibody levels among H. pylori-positive Japanese adults
- PMID: 24453409
- PMCID: PMC3881527
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/142358
Significant association between serum interleukin-6 and Helicobacter pylori antibody levels among H. pylori-positive Japanese adults
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine produced by many types of cells. Inflammation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis that is an underlying cause of coronary heart disease (CHD). Since the 1990s, some studies have shown an association between H. pylori infection and CHD, which may be mediated by inflammation. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the association between serum anti-H. pylori IgG levels and serum IL-6 levels in H. pylori-infected adults.
Methods: We enrolled 158 subjects who visited a clinic located in an urban area to be tested for H. pylori infection, using the (13)C-urea breath test, and who were found to be infected and subsequently received eradication.
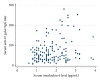
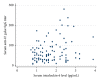
Results: The geometric mean serum IL-6 level was 1.78 pg/mL for men, 1.57 pg/mL for women, and 1.64 pg/mL overall. Logarithms of serum IL-6 levels were positively correlated with logarithms of serum H. pylori IgG levels (r = 0.24, P = 0.002). In multiple linear regression analysis adjusting for sex and age, the serum IL-6 level was still significantly associated with the IgG level in all subjects (β = 0.18, P = 0.012).
Conclusion: Higher H. pylori IgG levels were significantly associated with higher serum IL-6 levels among H. pylori-infected individuals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in coronary artery disease: influence of H. pylori eradication on coronary artery lumen after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. The detection of H. pylori specific DNA in human coronary atherosclerotic plaque.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001 Aug;52(1 Suppl 1):3-31. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11795863 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of Chlamydia pneumoniae, helicobacter pylori and cytomegalovirus in coronary artery disease.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2011 Apr;24(2):95-101. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2011. PMID: 21454155
-
Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and serum interleukin-18 in patients with carotid atherosclerosis.Helicobacter. 2013 Apr;18(2):124-8. doi: 10.1111/hel.12014. Epub 2012 Nov 4. Helicobacter. 2013. PMID: 23121308
-
Helicobacter pylori and CagA status, serum gastrin, interleukin-8 and gastric acid secretion in gastric cancer.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002 Aug;37(8):891-8. doi: 10.1080/003655202760230838. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12229962
-
Serum levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP)in Helicobacter pylori-infected peptic ulcer patients and its association with bacterial CagA virulence factor.Dig Dis Sci. 2009 Dec;54(12):2612-6. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0686-z. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19160050
Cited by
-
Serologically Determined Gastric Mucosal Condition Is a Predictive Factor for Osteoporosis in Japanese Men.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Jul;60(7):2063-9. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3576-1. Epub 2015 Feb 8. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25663243
-
Helicobacter pylori eradication improves the quality of life regardless of the treatment outcome: A multicenter prospective cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(52):e9507. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009507. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29384953 Free PMC article.
-
Differential cytokine expression in gastric tissues highlights helicobacter pylori's role in gastritis.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 1;14(1):7683. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58407-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38561502 Free PMC article.
-
Elderly women who received Helicobacter pylori-eradicating therapy have reduced risk of low skeletal muscle mass.Clin Interv Aging. 2015 Oct 30;10:1771-7. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S95007. eCollection 2015. Clin Interv Aging. 2015. PMID: 26586939 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Markers for the Detection of Gastric Precancerous Conditions.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;16(12):2254. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122254. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927959 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hirano T, Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Biological and clinical aspects of interleukin 6. Immunology Today. 1990;11(12):443–449. - PubMed
-
- Horii Y, Muraguchi A, Iwano M, et al. Involvement of IL-6 in mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Journal of Immunology. 1989;143(12):3949–3955. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;352(16):1685–1695. - PubMed
-
- Mehta JL, Saldeen TGP, Rand K. Interactive role of infection, inflammation and traditional risk factors in atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 1998;31(6):1217–1225. - PubMed
-
- Ikonomidis I, Stamatelopoulos K, Lekakis J, Vamvakou GD, Kremastinos DT. Inflammatory and non-invasive vascular markers: the multimarker approach for risk stratification in coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2008;199(1):3–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical