Clinical utility of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 24453498
- PMCID: PMC3890964
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S35901
Clinical utility of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
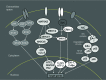
Immune/inflammatory cells act in rheumatoid arthritis (RA)-affected patients by synthesizing several inflammatory mediators, including cytokines that initiate intracellular signaling. Recently, small molecule inhibitors of transduction and transcription signals that influence the intracellular pathways (such as the Janus kinase [JAK] family of tyrosine kinases) have been tested for RA treatment. Four members of the JAK family are known: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TyK2. JAK1/JAK3 constitutively binds to the cytoplasmic portion of the cytokine receptor - the common gamma chain - that represents a common subunit of several cytokines involved in T-cell and natural killer cell development, as well as in B-cell activation. Tofacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor that is now available and effective in RA treatment, as shown in multiple Phase II and Phase III clinical trials. However, long-term safety data and comparisons with other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and small molecule inhibitors are necessary to better determine the role of tofacitinib in RA.
Keywords: Janus kinase inhibitors; intracellular signaling; kinases; rheumatoid arthritis; small molecules inhibitors; tofacitinib.
Figures

References
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205–2219. - PubMed
-
- Emery P, Dörner T. Optimising treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: a review of potential biological markers of response. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(12):2063–2070. - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Trentham DE, Fraser PA, et al. Long-term prospective trial of low-dose methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31(2):167–175. - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann R. Novel small-molecular therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012;24(3):335–341. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

