Asymmetrical hip bone density in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 24453704
- PMCID: PMC3882945
- DOI: 10.7224/1537-2073-13.1.43
Asymmetrical hip bone density in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
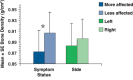
As multiple sclerosis (MS) may affect one leg more than the other, we predicted that bone mineral density (BMD) would be lower in the limb self-identified as more affected. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine whether ambulatory individuals with MS displaying moderate-to-severe lower-extremity paresis exhibit asymmetrical femoral neck BMD. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry was used to assess proximal femoral neck BMD. Lower BMD was observed in the proximal femoral neck of the more paretic limb (P = .001) in a group (N = 23) of ambulatory individuals with relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS). Our preliminary findings suggest that bilateral hip screening may be important in the early detection of compromised bone health in ambulatory individuals with RRMS. Further research is warranted to fully characterize the factors and mechanisms associated with bone loss and identify effective strategies for optimizing bone health in people with MS.
Figures
References
-
- Lips P, van Ginkel FC, Netelenbos JC, Wiersinga A, van der Vijgh WJ. Lower mobility and markers of bone resorption in the elderly. Bone Miner. 1990;9:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Formica CA, Cosman F, Nieves J, Herbert J, Lindsay R. Reduced bone mass and fat-free mass in women with multiple sclerosis: effects of ambulatory status and glucocorticoid use. Calcif Tissue Int. 1997;61:129–133. - PubMed
-
- Hearn AP, Silber E. Osteoporosis in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2010;16:1031–1043. - PubMed
-
- Ozgocmen S, Bulut S, Ilhan N, Gulkesen A, Ardicoglu O, Ozkan Y. Vitamin D deficiency and reduced bone mineral density in multiple sclerosis: effect of ambulatory status and functional capacity. J Bone Miner Metab. 2005;23:309–313. - PubMed
-
- Weinstock-Guttman B, Gallagher E, Baier M, et al. Risk of bone loss in men with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2004;10:170–175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials