Differentiation of neuromyelitis optica from multiple sclerosis on spinal magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 24453753
- PMCID: PMC3882989
- DOI: 10.7224/1537-2073-14.4.209
Differentiation of neuromyelitis optica from multiple sclerosis on spinal magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
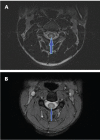
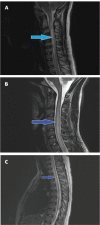
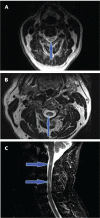
In order to examine the accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica (NMO) versus multiple sclerosis (MS), we performed a retrospective, rater-blinded review of 29 cases of NMO and 30 cases of MS using the criteria of long (more than three vertebral levels), continuous lesions with a central cord location for NMO and more peripheral and patchy lesions for MS. Using these criteria, two raters were able to distinguish the two conditions with a good degree of confidence, particularly when the imaging was performed at the time of an acute cord attack. The sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of NMO were 86.2% and 93.3%, respectively, for Rater A and 96.4% and 78.6%, respectively, for Rater B, with a kappa value of 0.72. Thus there are significant differences in lesion characteristics that allow the distinction on spinal cord imaging between MS and NMO with a moderately high degree of confidence. The location of the lesion as evident on MRI of the spine can be regarded as a distinguishing diagnostic feature between MS and NMO.
Figures
References
-
- Rodriguez M. Have we finally identified an autoimmune demyelinating disease? Neurology. 2009;66:572–573. - PubMed
-
- Wingerchuk DM,, Hogancamp WF,, O'Brien PC,, Weinshenker BG. The clinical course of neuromyelitis optica (Devic's syndrome) Neurology. 1999;53:1107–1114. - PubMed
-
- Cree BAC,, Goodin DS,, Hauser SL. Neuromyelitis optica [review] Semin Neurol. 2002;22:105–122. - PubMed
-
- Wingerchuk DM. Neuromyelitis optica: current concepts. Front Biosci. 2004;9:834–840. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
