Genetic variants of neurotransmitter-related genes and miRNAs in Egyptian autistic patients
- PMID: 24453887
- PMCID: PMC3885205
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/670621
Genetic variants of neurotransmitter-related genes and miRNAs in Egyptian autistic patients
Abstract
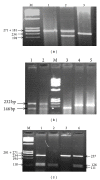
Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder with indisputable evidence for a genetic component. This work studied the association of autism with genetic variations in neurotransmitter-related genes, including MAOA uVNTR, MAOB rs1799836, and DRD2 TaqI A in 53 autistic patients and 30 healthy individuals. The study also analyzed sequence variations of miR-431 and miR-21. MAOA uVNTR was genotyped by PCR, MAOB and DRD2 polymorphisms were analyzed by PCR-based RFLP, and miR-431 and miR-21 were sequenced. Low expressing allele of MAOA uVNTR was frequently higher in female patients compared to that in controls (OR = 2.25). MAOB G allele frequency was more significantly increased in autistic patients than in controls (P < 0.001 for both males and females). DRD2 A1+ genotype increased autism risk (OR = 5.1). Severity of autism tends to be slightly affected by MAOA/B genotype. Plasma MAOB activity was significantly reduced in G than in A allele carrying males. There was no significant difference in patients and maternal plasma MAOA/B activity compared to controls. Neither mutations nor SNPs in miR-431 and miR-21 were found among studied patients. This study threw light on some neurotransmitter-related genes suggesting their potential role in Autism pathogenesis that warrants further studies and much consideration.
Figures
References
-
- Chakrabarti S, Fombonne E. Pervasive developmental disorders in preschool children: confirmation of high prevalence. American Journal of Psychiatry. 2005;162(6):1133–1141. - PubMed
-
- Cohen IL, Liu X, Schutz C, et al. Association of autism severity with a monoamine oxidase A functional polymorphism. Clinical Genetics. 2003;64(3):190–197. - PubMed
-
- Cohen IL, Liu X, Lewis MES, et al. Autism severity is associated with child and maternal MAOA genotypes. Clinical Genetics. 2011;79(4):355–362. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

