Lu/BCAM adhesion glycoprotein is a receptor for Escherichia coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1)
- PMID: 24453976
- PMCID: PMC3894216
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003884
Lu/BCAM adhesion glycoprotein is a receptor for Escherichia coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1)
Erratum in
- PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jan;10(1). doi:10.1371/annotation/6eec6403-e090-4283-aa34-34cc58ca0bbb
Abstract
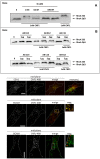
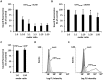
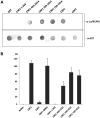
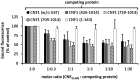
The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) is a protein toxin which is a major virulence factor of pathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Here, we identified the Lutheran (Lu) adhesion glycoprotein/basal cell adhesion molecule (BCAM) as cellular receptor for CNF1 by co-precipitation of cell surface molecules with tagged toxin. The CNF1-Lu/BCAM interaction was verified by direct protein-protein interaction analysis and competition studies. These studies revealed amino acids 720 to 1014 of CNF1 as the binding site for Lu/BCAM. We suggest two cell interaction sites in CNF1: first the N-terminus, which binds to p37LRP as postulated before. Binding of CNF1 to p37LRP seems to be crucial for the toxin's action. However, it is not sufficient for the binding of CNF1 to the cell surface. A region directly adjacent to the catalytic domain is a high affinity interaction site for Lu/BCAM. We found Lu/BCAM to be essential for the binding of CNF1 to cells. Cells deficient in Lu/BCAM but expressing p37LRP could not bind labeled CNF1. Therefore, we conclude that LRP and Lu/BCAM are both required for toxin action but with different functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Analysing the Structural Effect of Point Mutations of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) on Lu/BCAM Adhesion Glycoprotein Association.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Mar 13;10(3):122. doi: 10.3390/toxins10030122. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29533999 Free PMC article.
-
High Affinity Binding of Escherichia coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) to Lu/BCAM Adhesion Glycoprotein.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Dec 21;10(1):3. doi: 10.3390/toxins10010003. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29267242 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role for the Lu/BCAM-spectrin interaction in actin cytoskeleton reorganization.Biochem J. 2011 Jun 15;436(3):699-708. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101717. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21434869
-
The Role of Lutheran/Basal Cell Adhesion Molecule in Hematological Diseases and Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 2;25(13):7268. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137268. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel receptors for bacterial protein toxins.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Feb;23:55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.11.003. Epub 2014 Nov 22. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25461573 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of pks+ Escherichia coli (E. coli) to Colon Carcinogenesis.Microorganisms. 2024 May 30;12(6):1111. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061111. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C910 chemical compound inhibits the traffiking of several bacterial AB toxins with cross-protection against influenza virus.iScience. 2022 Jun 6;25(7):104537. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104537. eCollection 2022 Jul 15. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35769882 Free PMC article.
-
Analysing the Structural Effect of Point Mutations of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) on Lu/BCAM Adhesion Glycoprotein Association.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Mar 13;10(3):122. doi: 10.3390/toxins10030122. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29533999 Free PMC article.
-
High Affinity Binding of Escherichia coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) to Lu/BCAM Adhesion Glycoprotein.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Dec 21;10(1):3. doi: 10.3390/toxins10010003. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29267242 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrative Computational Approach for the Prediction of Human-Plasmodium Protein-Protein Interactions.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 19;2020:2082540. doi: 10.1155/2020/2082540. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33426052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ulett GC, Totsika M, Schaale K, Carey AJ, Sweet MJ, et al. (2013) Uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence and innate immune responses during urinary tract infection. Curr Opin Microbiol 16: S1369–5274. - PubMed
-
- Khan NA, Wang Y, Kim KJ, Chung JW, Wass CA, et al. (2002) Cytotoxic necrotizing factor-1 contributes to Escherichia coli K1 invasion of the central nervous system. J Biol Chem 277: 15607–15612. - PubMed
-
- Flatau G, Lemichez E, Gauthier M, Chardin P, Paris S, et al. (1997) Toxin-induced activation of the G protein p21 Rho by deamidation of glutamine. Nature 387: 729–733. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt G, Sehr P, Wilm M, Selzer J, Mann M, et al. (1997) Gln63 of Rho is deamidated by Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1. Nature 387: 725–729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

