N-(4-Meth-oxy-phen-yl)-6-methyl-2-phenyl-5-{[4-(tri-fluoro-meth-yl)anilino]meth-yl}pyrimidin-4-amine
- PMID: 24454254
- PMCID: PMC3885078
- DOI: 10.1107/S160053681303170X
N-(4-Meth-oxy-phen-yl)-6-methyl-2-phenyl-5-{[4-(tri-fluoro-meth-yl)anilino]meth-yl}pyrimidin-4-amine
Abstract
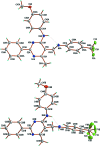
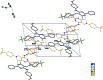
The title compound, C26H23F3N4O, crystallizes with two symmetry-independent mol-ecules in the asymmetric unit, denoted A and B, which differ mainly in the rotation of the meth-oxy-phenyl ring. The -CF3 group of mol-ecule B is disordered by rotation, with the F atoms split over two sets of sites; the occupancy factor for the major component is 0.853 (4). The dihedral angles between the pyrimidine ring and the attached phenyl, meth-oxy-phenyl and tri-fluoro-methyl-phenyl rings are 8.1 (2), 37.5 (2) and 70.7 (2)°, respectively, in mol-ecule A, and 9.3 (2), 5.3 (2) and 79.7 (2)° in mol-ecule B. An intra-molecular N-H⋯N hydrogen bond occurs in each mol-ecule. In the crystal, two crystallographically independent mol-ecules associate into a dimer via a pair of N-H⋯N hydrogen bonds, with a resulting R 2 (2)(12) ring motif and π-π stacking inter-actions [centroid-centroid distance = 3.517 (4) Å] between the pyrimidine rings. For the A mol-ecules, there are inter-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds between an aryl C atom of meth-oxy-phenyl ring and a meth-oxy O atom of an adjacent mol-ecule. A similar inter-action is lacking in the B mol-ecules.
Figures
References
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2005). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Cieplik, J., Machoń, Z., Zimecki, M. & Wieczorek, Z. (1995). Il Farmaco, 50, 131–136.
-
- Cieplik, J., Pluta, J., Bryndal, I. & Lis, T. (2006). Acta Cryst. C62, o259–o261. - PubMed
-
- Cieplik, J., Raginia, M., Pluta, J., Gubrynowicz, O., Bryndal, I. & Lis, T. (2008). Acta Pol. Pharm. 65, 427–434. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
