The multifaceted role of Th17 lymphocytes and their associated cytokines in cancer
- PMID: 24454480
- PMCID: PMC3888704
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/957878
The multifaceted role of Th17 lymphocytes and their associated cytokines in cancer
Abstract
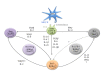
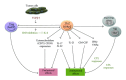
While the role of T helper 17 lymphocytes (Th17) in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and in infectious immunity has been relatively well defined, the impact of these cells and their associated cytokines on cancer development is still under debate. Although multiple reports have indicated that Th17 can promote anticancer immunity, others have argued that these cells may exhibit tumor-promoting properties. This dichotomy in the function of Th17 lymphocytes in cancer may be related to the versatile nature of these cells, being capable of differentiating into either proinflammatory Th1 or suppressive FoxP3-expressing Treg cells or hybrid T cell subsets depending on the underlying environmental conditions. In the current review, we examine the role of Th17 lymphocytes and Th17-associated cytokines in cancer and discuss how factors that control their final lineage commitment decision may influence the balance between their tumor-promoting versus tumor-suppressing properties.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

