Cerebrospinal fluid pharmacology: an improved pharmacology approach for chinese herbal medicine research
- PMID: 24454505
- PMCID: PMC3876922
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/674305
Cerebrospinal fluid pharmacology: an improved pharmacology approach for chinese herbal medicine research
Abstract
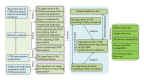
Despite many successful applications of Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) in the treatment and prevention of neurological diseases (ND), the fully scientific understanding of CHM's action mechanisms had been hampered for lack of appropriate methods to explore the combinatorial rules, the synergistic mechanisms, and the molecular basis of CHM. As an improved pharmacology approach, cerebrospinal fluid pharmacology (CSFP), based on the fact that cerebrospinal fluid plays an important role in the health maintenance of specific survival environment for neurons and glial cells, has been constructed and applied to CHM research for treating ND. In the present review, the concept and advantages of CSFP are briefly introduced. The approaches and key technologies of CSFP in CHM research are also collated and analyzed. Furthermore, the developing tendency of CSFP is summarized, and its framework in CHM research is also proposed. In summary, CSFP provides a new strategy not only to eliminate some barriers of CHM research for treating ND, but also to broaden the pharmacology research for bridging the gap between CHM and modern medicine. Moreover, the advancements in CSFP will bring about a conceptual move in active ingredients discovery of CHM and make a significant contribution to CHM modernization and globalization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology: a new approach for chinese herbal medicine research.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:621423. doi: 10.1155/2013/621423. Epub 2013 May 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23762149 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine for anxiety and depression in patients with diarrheal irritable bowel syndrome based on network pharmacology and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 21;15:1404738. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1404738. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38835657 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing active ingredient biosynthesis in Chinese herbal medicine: biotechnological strategies and molecular mechanisms.PeerJ. 2025 Feb 10;13:e18914. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18914. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 39950047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network Pharmacology-Based and Clinically Relevant Prediction of the Potential Targets of Chinese Herbs in Ovarian Cancer Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 8;2020:8965459. doi: 10.1155/2020/8965459. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33150184 Free PMC article.
-
A novel strategy for active compound efficacy status identification in multi-tropism Chinese herbal medicine (Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi) based on multi-indexes spectrum-effect gray correlation analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;300:115677. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115677. Epub 2022 Sep 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36064148
Cited by
-
Naoxintong Protects Primary Neurons from Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation Induced Injury through PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:5815946. doi: 10.1155/2016/5815946. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 26949405 Free PMC article.
-
Examination and Estimation of Anticholinergic Burden: Current Trends and Implications for Future Research.Drugs Aging. 2016 May;33(5):305-13. doi: 10.1007/s40266-016-0362-5. Drugs Aging. 2016. PMID: 27038065
-
An overview of pharmacodynamic modelling, ligand-binding approach and its application in clinical practice.Saudi Pharm J. 2017 Feb;25(2):165-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.07.002. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Saudi Pharm J. 2017. PMID: 28344466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jiang M, Yang J, Zhang C, et al. Clinical studies with traditional Chinese medicine in the past decade and future research and development. Planta Medica. 2010;76(17):2048–2064. - PubMed
-
- Lin C-H, Chang T-T, Sun M-F, et al. Potent inhibitor design against H1N1 swine influenza: Structure-based and molecular dynamics analysis for M2 inhibitors from traditional Chinese medicine database. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics. 2011;28(4):471–482. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

