Patient and healthcare provider barriers to hypertension awareness, treatment and follow up: a systematic review and meta-analysis of qualitative and quantitative studies
- PMID: 24454721
- PMCID: PMC3893097
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084238
Patient and healthcare provider barriers to hypertension awareness, treatment and follow up: a systematic review and meta-analysis of qualitative and quantitative studies
Abstract
Background: Although the importance of detecting, treating, and controlling hypertension has been recognized for decades, the majority of patients with hypertension remain uncontrolled. The path from evidence to practice contains many potential barriers, but their role has not been reviewed systematically. This review aimed to synthesize and identify important barriers to hypertension control as reported by patients and healthcare providers.
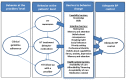
Methods: Electronic databases MEDLINE, EMBASE and Global Health were searched systematically up to February 2013. Two reviewers independently selected eligible studies. Two reviewers categorized barriers based on a theoretical framework of behavior change. The theoretical framework suggests that a change in behavior requires a strong commitment to change [intention], the necessary skills and abilities to adopt the behavior [capability], and an absence of health system and support constraints.
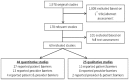
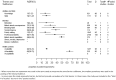
Findings: Twenty-five qualitative studies and 44 quantitative studies met the inclusion criteria. In qualitative studies, health system barriers were most commonly discussed in studies of patients and health care providers. Quantitative studies identified disagreement with clinical recommendations as the most common barrier among health care providers. Quantitative studies of patients yielded different results: lack of knowledge was the most common barrier to hypertension awareness. Stress, anxiety and depression were most commonly reported as barriers that hindered or delayed adoption of a healthier lifestyle. In terms of hypertension treatment adherence, patients mostly reported forgetting to take their medication. Finally, priority setting barriers were most commonly reported by patients in terms of following up with their health care providers.
Conclusions: This review identified a wide range of barriers facing patients and health care providers pursuing hypertension control, indicating the need for targeted multi-faceted interventions. More methodologically rigorous studies that encompass the range of barriers and that include low- and middle-income countries are required in order to inform policies to improve hypertension control.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization (2009) Global health risks: Mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks. Geneva: World Health Organization.
-
- Chow CK, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, Islam S, Gupta R, et al. (2013) Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-, middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA 310 (9) 959–68. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, et al. (2003) The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: The JNC 7 report. JAMA 289 (19) 2560–72. - PubMed
-
- Nieuwlaat R, Schwalm JD, Khatib R, Yusuf S (2013) Why are we failing to implement effective therapies in cardiovascular disease? Eur Heart J 34 (17) 1262–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

