Multi-modal use of a socially directed call in bonobos
- PMID: 24454745
- PMCID: PMC3893130
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084738
Multi-modal use of a socially directed call in bonobos
Abstract
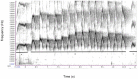
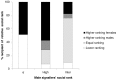
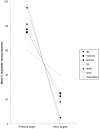
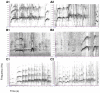
'Contest hoots' are acoustically complex vocalisations produced by adult and subadult male bonobos (Pan paniscus). These calls are often directed at specific individuals and regularly combined with gestures and other body signals. The aim of our study was to describe the multi-modal use of this call type and to clarify its communicative and social function. To this end, we observed two large groups of bonobos, which generated a sample of 585 communicative interactions initiated by 10 different males. We found that contest hooting, with or without other associated signals, was produced to challenge and provoke a social reaction in the targeted individual, usually agonistic chase. Interestingly, 'contest hoots' were sometimes also used during friendly play. In both contexts, males were highly selective in whom they targeted by preferentially choosing individuals of equal or higher social rank, suggesting that the calls functioned to assert social status. Multi-modal sequences were not more successful in eliciting reactions than contest hoots given alone, but we found a significant difference in the choice of associated gestures between playful and agonistic contexts. During friendly play, contest hoots were significantly more often combined with soft than rough gestures compared to agonistic challenges, while the calls' acoustic structure remained the same. We conclude that contest hoots indicate the signaller's intention to interact socially with important group members, while the gestures provide additional cues concerning the nature of the desired interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hauser MD, Chomsky N, Fitch WT (2002) The faculty of language: What is it, who has it, and how did it evolve? Science 298: 1569–1579. - PubMed
-
- de Waal FB (2003) Darwin's Legacy and the study of primate visual communication. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1000: 7–31. - PubMed
-
- Call J, Tomasello M (2007) The gestural communication of apes and monkeys. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
-
- Crockford C, Wittig RM, Mundry R, Zuberbühler K (2012) Wild chimpanzees inform ignorant group members of danger. Curr Biol 22: 142–146. - PubMed
-
- Seyfarth RM, Cheney DL (2010) Production, usage, and comprehension in animal vocalizations. Brain Lang 115: 92–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

