Atp6v1c1 may regulate filament actin arrangement in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24454753
- PMCID: PMC3893128
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084833
Atp6v1c1 may regulate filament actin arrangement in breast cancer cells
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(1). doi:10.1371/annotation/ca9f2d5b-93ab-4d7c-b577-cd045b343e53
Abstract
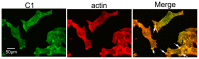
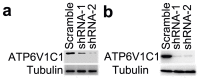
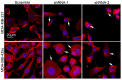
Previous studies have shown that the rate of breast cancer metastasis correlates with the expression of vacuolar H(+)-ATPases (V-ATPases). However, how V-ATPase is involved in breast cancer metastasis remains unknown. Our previous study showed that Atp6v1c1-depleted osteoclasts did not form organized actin rings and that Atp6v1c1 co-localizes with F-actin. In this study, we found that the normal arrangement of filamentous actin is disrupted in Atp6v1c1-depleted 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells and in the ATP6V1C1-depleted human breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435s. We further found that Atp6v1c1 co-localizes with F-actin in 4T1 cells. The results of our study suggest that high expression of Atp6v1c1 affects the actin structure of cancer cells such that it facilitates breast cancer metastasis. The findings also indicate that Atp6v1c1 could be a novel target for breast cancer metastasis therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Osteoclast proton pump regulator Atp6v1c1 enhances breast cancer growth by activating the mTORC1 pathway and bone metastasis by increasing V-ATPase activity.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 18;8(29):47675-47690. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17544. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28504970 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of atp6v1c1 prevents breast cancer growth and bone metastasis.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Sep 5;9(8):853-62. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6030. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24155661 Free PMC article.
-
Atp6v1c1 is an essential component of the osteoclast proton pump and in F-actin ring formation in osteoclasts.Biochem J. 2009 Jan 1;417(1):195-203. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081073. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 18657050 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of V-ATPase assembly and function of V-ATPases in tumor cell invasiveness.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Aug;1857(8):1213-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2016.02.010. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26906430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational identification of enoxacin as a novel V-ATPase-directed osteoclast inhibitor.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Mar;13(2):180-91. doi: 10.2174/138920312800493151. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22044158 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation and function of V-ATPases in physiology and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Dec 1;1862(12):183341. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183341. Epub 2020 May 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32422136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Atp6v1c1 Prevents Inflammation and Bone Erosion Caused by Periodontitis and Reveals Its Critical Function in Osteoimmunology.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 14;10(8):e0134903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134903. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26274612 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes: Insights from Retinoblastoma and Other Eye Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 25;21(19):7055. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197055. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32992741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-cancer V-ATPase molecular signatures: A distinctive balance of subunit C isoforms in esophageal carcinoma.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jan;51:102581. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.042. Epub 2020 Jan 3. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 31901859 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Insights into the Structure, Regulation, and Function of the V-ATPases.Trends Biochem Sci. 2015 Oct;40(10):611-622. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.08.005. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015. PMID: 26410601 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sennoune SR, Bakunts K, Martinez GM, Chua-Tuan JL, Kebir Y, et al. (2004) Vacuolar H+-ATPase in human breast cancer cells with distinct metastatic potential: distribution and functional activity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286: C1443–C1452. - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Zaguilan R, Raghunand N, Lynch RM, Bellamy W, Martinez GM, et al. (1999) pH and drug resistance. I. Functional expression of plasmalemmal V-type H+-ATPase in drug-resistant human breast carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol 57: 1037–1046. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Cheng T, Feng HT, Pavlos NJ, Zheng MH (2007) Structure and function of V-ATPases in osteoclasts: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of osteolysis. Histol Histopathol 22: 443–454. - PubMed
-
- Forgac M (2007) Vacuolar ATPases: rotary proton pumps in physiology and pathophysiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 917–929. - PubMed
-
- Forgac M (1999) Structure and properties of the vacuolar (H+)-ATPases. J Biol Chem 274: 12951–12954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

