Proteomic analysis of cellular response induced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes exposure in A549 cells
- PMID: 24454774
- PMCID: PMC3891800
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084974
Proteomic analysis of cellular response induced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes exposure in A549 cells
Abstract
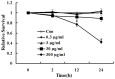
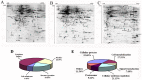
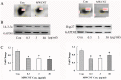
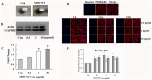
The wide application of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) has raised serious concerns about their safety on human health and the environment. However, the potential harmful effects of MWCNT remain unclear and contradictory. To clarify the potentially toxic effects of MWCNT and to elucidate the associated underlying mechanisms, the effects of MWCNT on human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells were examined at both the cellular and the protein level. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity were examined, followed by a proteomic analysis (2-DE coupled with LC-MS/MS) of the cellular response to MWCNT. Our results demonstrate that MWCNT induces cytotoxicity in A549 cells only at relatively high concentrations and longer exposure time. Within a relatively low dosage range (30 µg/ml) and short time period (24 h), MWCNT treatment does not induce significant cytotoxicity, cell cycle changes, apoptosis, or DNA damage. However, at these low doses and times, MWCNT treatment causes significant changes in protein expression. A total of 106 proteins show altered expression at various time points and dosages, and of these, 52 proteins were further identified by MS. Identified proteins are involved in several cellular processes including proliferation, stress, and cellular skeleton organization. In particular, MWCNT treatment causes increases in actin expression. This increase has the potential to contribute to increased migration capacity and may be mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


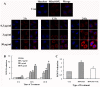

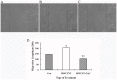
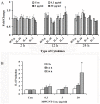
References
-
- Tretyakov YD, Goodilin EA (2009) Key trends in basic and application-oriented research on nanomaterials. Russ Chem Rev 78: 801–820 10.1070/RC2009v078n09ABEH004029 - DOI
-
- He L, Toh CS (2006) Recent advances in analytical chemistry–a material approach. Anal Chim Acta 556: 1–15. PubMed: 17723326. - PubMed
-
- Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354: 56–58 10.1038/354056a0 - DOI
-
- Murr LE, Bang JJ, Esquivel PA, Guerrero PA, Lopez DA (2004) Carbon nanotubes, nanocrystal forms and complex nanoparticle aggregates in common fuel-gas combustion source and ambient air. J Nanoparticle Res 6: 241–251.
-
- Endo M (1988) Grow carbon fibers in the vapor phase. Chem Tech 18: 568–576.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

