E2A predicts prognosis of colorectal cancer patients and regulates cancer cell growth by targeting miR-320a
- PMID: 24454819
- PMCID: PMC3890311
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085201
E2A predicts prognosis of colorectal cancer patients and regulates cancer cell growth by targeting miR-320a
Abstract
Background and objective: Transcriptional factor E2A is crucial for the normal development and differentiation of B and T lymphocytes. Dysregulation of E2A leads to leukemia and tumorigenesis of some solid tumors. The expression and clinical significance of E2A as well as its role in colorectal cancer (CRC) are still unknown. This study aims to assess E2A expression in CRC tissues, evaluate its prognosis value, and investigate its role in colon cancer cell growth.
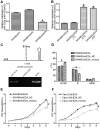
Methods: E2A expression in CRC tissues and normal mucosa was detected by immunohistochemical staining; Kaplan-Meier survival curve and Cox regression model were used to evaluate the prognostic value of E2A. Lentivirus was used to construct E2A stably knocked-down cells. MTT assay was employed to detect cell proliferation change; cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry; and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was used to validate the predicted binding target of E2A.
Results: Expression of E2A was lower in CRC tissues than normal mucosa; low E2A expression correlated with advanced TNM stage and larger tumor size, and predicted poor prognosis of CRC patients. E2A knockdown resulted in increased cell proliferation rate and cell cycle acceleration. ChIP assay showed miR-320a was a direct target of E2A and upregulation of miR-320a in E2A downregulated cells could reverse cell proliferation and cell cycle changes caused by E2A deficiency.
Conclusions: E2A is an independent prognostic factor for CRC patients and targets miR-320a to regulate cell proliferation of colon cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of microRNA-16 expression in human colorectal cancer.World J Surg. 2013 Dec;37(12):2944-9. doi: 10.1007/s00268-013-2205-4. World J Surg. 2013. PMID: 24045965
-
MiR-769 Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting HEY1.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Dec 19;24:9232-9239. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911663. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30565566 Free PMC article.
-
miR-422a is an independent prognostic factor and functions as a potential tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 28;22(24):5589-97. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i24.5589. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27350737 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of microRNA-124 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with colorectal cancer.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013 Feb;28(2):183-9. doi: 10.1007/s00384-012-1550-3. Epub 2012 Aug 11. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013. PMID: 22885837
-
MiR-194, commonly repressed in colorectal cancer, suppresses tumor growth by regulating the MAP4K4/c-Jun/MDM2 signaling pathway.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(7):1046-58. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1007767. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25602366 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA 320, an Anti-Oncogene Target miRNA for Cancer Therapy.Biomedicines. 2021 May 23;9(6):591. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060591. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34071109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of E2A in mid-secretory endometrium of women suffering from recurrent miscarriage.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Dec;37(6):910-914. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1826-5. Epub 2017 Dec 21. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29270752
-
MicroRNA as a Prognostic and Diagnostic Marker in T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 18;22(10):5317. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105317. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross Platform Standardisation of an Experimental Pipeline for Use in the Identification of Dysregulated Human Circulating MiRNAs.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 10;10(9):e0137389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137389. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26355751 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the CREB1-miRNA feedback loop in human malignancies.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):8487-502. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5050-x. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27059735 Review.
References
-
- Bain G, Maandag EC, Izon DJ, Amsen D, Kruisbeek AM, et al. (1994) E2A proteins are requiredfor proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell 79: 885–892. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang Y, Soriano P, Weintraub H (1994) The helix-loop-helix gene E2A is required for B cell formation. Cell 79: 875–884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

