Age related differences in dynamics of specific memory B cell populations after clinical pertussis infection
- PMID: 24454823
- PMCID: PMC3890308
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085227
Age related differences in dynamics of specific memory B cell populations after clinical pertussis infection
Abstract
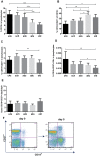
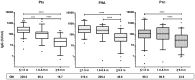
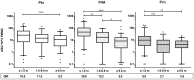
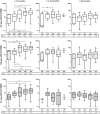
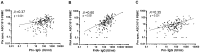
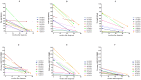
For a better understanding of the maintenance of immune mechanisms to Bordetella pertussis (Bp) in relation to age, we investigated the dynamic range of specific B cell responses in various age-groups at different time points after a laboratory confirmed pertussis infection. Blood samples were obtained in a Dutch cross sectional observational study from symptomatic pertussis cases. Lymphocyte subpopulations were phenotyped by flowcytometry before and after culture. Memory B (Bmem) cells were differentiated into IgG antibody secreting cells (ASC) by polyclonal stimulation and detected by an ELISPOT assay specific for pertussis antigens pertussis toxin (Ptx), filamentous haemagglutinin (FHA) and pertactin (Prn). Bp antigen specific IgG concentrations in plasma were determined using multiplex technology. The majority of subjects having experienced a clinical pertussis episode demonstrated high levels of both Bp specific IgG and Bmem cell levels within the first 6 weeks after diagnosis. Significantly lower levels were observed thereafter. Waning of cellular and humoral immunity to maintenance levels occurred within 9 months after antigen encounter. Age was found to determine the maximum but not base-line frequencies of Bmem cell populations; higher levels of Bmem cells specific for Ptx and FHA were reached in adults and (pre-) elderly compared to under-fours and schoolchildren in the first 6 weeks after Bp exposure, whereas not in later phases. This age effect was less obvious for specific IgG levels. Nonetheless, subjects' levels of specific Bmem cells and specific IgG were weakly correlated. This is the first study to show that both age and closeness to last Bp encounter impacts the size of Bp specific Bmem cell and plasma IgG levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Waning and aging of cellular immunity to Bordetella pertussis.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv071. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv071. Epub 2015 Sep 13. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26371178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired long-term maintenance and function of Bordetella pertussis specific B cell memory.Vaccine. 2010 Sep 14;28(40):6637-46. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.06.118. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20637762
-
Identifying long-term memory B-cells in vaccinated children despite waning antibody levels specific for Bordetella pertussis proteins.Vaccine. 2011 Feb 4;29(7):1431-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.12.033. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21187178
-
Impact of infant and preschool pertussis vaccinations on memory B-cell responses in children at 4 years of age.Vaccine. 2011 Aug 5;29(34):5725-30. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.05.094. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21669247
-
The Importance of Monitoring Antigen-Specific Memory B Cells, and How ImmunoSpot Assays Are Suitable for This Task.Cells. 2025 Feb 5;14(3):223. doi: 10.3390/cells14030223. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39937014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Memory B Cell Activation Induced by Pertussis Booster Vaccination in Four Age Groups of Three Countries.Front Immunol. 2022 May 23;13:864674. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.864674. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35677044 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antibody-mediated rejection in pediatric kidney transplantation: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management.Drugs. 2015 Apr;75(5):455-72. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0369-y. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25813498 Review.
-
Factors influencing long-term persistence of anti-HBs after hepatitis B vaccination.NPJ Vaccines. 2022 Dec 26;7(1):173. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00596-5. NPJ Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 36572682 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Bordetella pertussis-specific CD4+ T-Cell Responses at Older Age.Front Aging. 2022 Feb 2;2:737870. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2021.737870. eCollection 2021. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 35822011 Free PMC article.
-
Waning and aging of cellular immunity to Bordetella pertussis.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv071. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv071. Epub 2015 Sep 13. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26371178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Taranger J, Trollfors B, Bergfors E, Knutsson N, Sundh V, et al. (2001) Mass vaccination of children with pertussis toxoid–decreased incidence in both vaccinated and nonvaccinated persons. Clin Infect Dis 33: 1004–1010. - PubMed
-
- Rashid H, Khandaker G, Booy R (2012) Vaccination and herd immunity: what more do we know? Curr Opin Infect Dis 25: 243–249. - PubMed
-
- Preziosi MP, Halloran ME (2003) Effects of pertussis vaccination on disease: vaccine efficacy in reducing clinical severity. Clin Infect Dis 37: 772–779. - PubMed
-
- Hewlett EL, Edwards KM (2005) Clinical practice. Pertussis–not just for kids. N Engl J Med 352: 1215–1222. - PubMed
-
- de Greeff SC, Mooi FR, Schellekens JF, de Melker HE (2008) Impact of acellular pertussis preschool booster vaccination on disease burden of pertussis in The Netherlands. Pediatr Infect Dis J 27: 218–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

