Hindlimb suspension and SPE-like radiation impairs clearance of bacterial infections
- PMID: 24454913
- PMCID: PMC3893249
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085665
Hindlimb suspension and SPE-like radiation impairs clearance of bacterial infections
Abstract
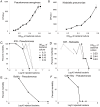
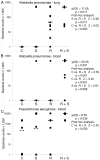
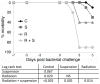
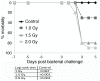
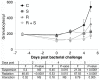
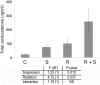
A major risk of extended space travel is the combined effects of weightlessness and radiation exposure on the immune system. In this study, we used the hindlimb suspension model of microgravity that includes the other space stressors, situational and confinement stress and alterations in food intake, and solar particle event (SPE)-like radiation to measure the combined effects on the ability to control bacterial infections. A massive increase in morbidity and decrease in the ability to control bacterial growth was observed using 2 different types of bacteria delivered by systemic and pulmonary routes in 3 different strains of mice. These data suggest that an astronaut exposed to a strong SPE during extended space travel is at increased risk for the development of infections that could potentially be severe and interfere with mission success and astronaut health.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

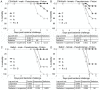
References
-
- Meehan R, Whitson P, Sams C (1993) The role of psychoneuroendocrine factors on spaceflight-induced immunological alterations. J Leukoc Biol 54: 236–244. - PubMed
-
- Aponte VM, Finch DS, Klaus DM (2006) Considerations for non-invasive in-flight monitoring of astronaut immune status with potential use of MEMS and NEMS devices. Life Sci 79: 1317–1333. - PubMed
-
- Kita M, Yamamoto T, Imanishi J, Fuse A (2004) Influence of gravity changes induced by parabolic flight on cytokine production in mouse spleen. J Gravit Physiol 11: P67–68. - PubMed
-
- Sastry KJ, Nehete PN, Savary CA (2001) Impairment of antigen-specific cellular immune responses under simulated microgravity conditions. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37: 203–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

