An analysis of 1256 cases of sporadic ruptured cerebral aneurysm in a single Chinese institution
- PMID: 24454914
- PMCID: PMC3893225
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085668
An analysis of 1256 cases of sporadic ruptured cerebral aneurysm in a single Chinese institution
Abstract
Background: To review the epidemiology of sporadic ruptured cerebral aneurysm.
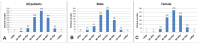
Methods: This is a retrospective study of consecutive 1256 Chinese patients between January 2006 and January 2013, who were admitted to the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, China, for spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage due to a rupture of cerebral artery aneurysm. In 288 males and 478 females, the size of aneurysms was measured by a neuroradiologist on DSA. In 123 males and 184 females, the size of the ruptured aneurysms was not measured. The remaining patients, with 61 males and 122 females, had multiple aneurysms, and the medical record could not reliably determine the specific aneurysm responsible for the rupture.
Results: In total there were 784 females and 472 males with a female/male ratio of 1.66. The female/male ratio was down to 0.50 for patients younger than 35 yrs. For both males and females, aneurysm rupture was most common during the age of 50-59 yrs. Ruptured aneurysms were mostly of 2 mm-5 mm in size (47.1%), followed by 5 mm-10 mm (39.7%). Ruptured single cerebral aneurysm occurred in anterior circulation in 95.0% of the cases, with 5.0% occurred in posterior circulation. Ruptured aneurysm most commonly occurred at posterior communicating artery (34.9%) and anterior communicating artery (29.5%). 183 cases (14.6%) had multiple aneurysms.
Conclusions: With younger patients, there is a male predominance in our series. Ninety percent of patients have ruptured aneurysms less than 10 mm in size.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pakarinen S (1967) Incidence, aetiology, and prognosis of primary subarachnoid haemorrhage. A study based on 589 cases diagnosed in a defined urban population during a defined period. Acta Neurol Scand 43: Suppl 29: 1–28. - PubMed
-
- Phillips LH 2nd, Whisnant JP, O'Fallon WM, Sundt TM Jr (1980) The unchanging pattern of subarachnoid hemorrhage in a community. Neurology 30: 1034–1040. - PubMed
-
- Rinkel GJ, Djibuti M, Algra A, van Gijn J (1998) Prevalence and risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review. Stroke 29: 251–256. - PubMed
-
- Dickey P, Nunes J, Bautista C, Goodrich I (1994) Intracranial aneurysms: size, risk of rupture, and prophylactic surgical treatment. Conn Med 58: 583–586. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical