The RNA chaperone Hfq impacts growth, metabolism and production of virulence factors in Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 24454955
- PMCID: PMC3893282
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086113
The RNA chaperone Hfq impacts growth, metabolism and production of virulence factors in Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
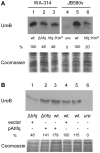
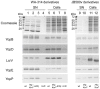
To adapt to changes in environmental conditions, bacteria regulate their gene expression at the transcriptional but also at the post-transcriptional level, e.g. by small RNAs (sRNAs) which modulate mRNA stability and translation. The conserved RNA chaperone Hfq mediates the interaction of many sRNAs with their target mRNAs, thereby playing a global role in fine-tuning protein production. In this study, we investigated the significance of Hfq for the enteropathogen Yersina enterocolitica serotype O:8. Hfq facilitated optimal growth in complex and minimal media. Our comparative protein analysis of parental and hfq-negative strains suggested that Hfq promotes lipid metabolism and transport, cell redox homeostasis, mRNA translation and ATP synthesis, and negatively affects carbon and nitrogen metabolism, transport of siderophore and peptides and tRNA synthesis. Accordingly, biochemical tests indicated that Hfq represses ornithine decarboxylase activity, indole production and utilization of glucose, mannitol, inositol and 1,2-propanediol. Moreover, Hfq repressed production of the siderophore yersiniabactin and its outer membrane receptor FyuA. In contrast, hfq mutants exhibited reduced urease production. Finally, strains lacking hfq were more susceptible to acidic pH and oxidative stress. Unlike previous reports in other Gram-negative bacteria, Hfq was dispensable for type III secretion encoded by the virulence plasmid. Using a chromosomally encoded FLAG-tagged Hfq, we observed increased production of Hfq-FLAG in late exponential and stationary phases. Overall, Hfq has a profound effect on metabolism, resistance to stress and modulates the production of two virulence factors in Y. enterocolitica, namely urease and yersiniabactin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Autenrieth IB, Firsching R (1996) Penetration of M cells and destruction of Peyer's patches by Y ersinia enterocolitica: an ultrastructural and histological study. J Med Microbiol 44: 285–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

