RHPS4 G-quadruplex ligand induces anti-proliferative effects in brain tumor cells
- PMID: 24454961
- PMCID: PMC3893285
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086187
RHPS4 G-quadruplex ligand induces anti-proliferative effects in brain tumor cells
Abstract
Background: Telomeric 3' overhangs can fold into a four-stranded DNA structure termed G-quadruplex (G4), a formation which inhibits telomerase. As telomerase activation is crucial for telomere maintenance in most cancer cells, several classes of G4 ligands have been designed to directly disrupt telomeric structure.
Methods: We exposed brain tumor cells to the G4 ligand 3,11-difluoro-6,8,13-trimethyl-8H-quino[4,3,2-kl]acridinium methosulfate (RHPS4) and investigated proliferation, cell cycle dynamics, telomere length, telomerase activity and activated c-Myc levels.
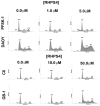
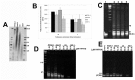
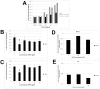
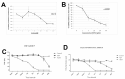
Results: Although all cell lines tested were sensitive to RHPS4, PFSK-1 central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal cells, DAOY medulloblastoma cells and U87 glioblastoma cells exhibited up to 30-fold increased sensitivity compared to KNS42 glioblastoma, C6 glioma and Res196 ependymoma cells. An increased proportion of S-phase cells were observed in medulloblastoma and high grade glioma cells whilst CNS PNET cells showed an increased proportion of G1-phase cells. RHPS4-induced phenotypes were concomitant with telomerase inhibition, manifested in a telomere length-independent manner and not associated with activated c-Myc levels. However, anti-proliferative effects were also observed in normal neural/endothelial cells in vitro and ex vivo.
Conclusion: This study warrants in vivo validation of RHPS4 and alternative G4 ligands as potential anti-cancer agents for brain tumors but highlights the consideration of dose-limiting tissue toxicities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Blackburn EH (1991) Structure and function of telomeres. Nature 350: 569–573. - PubMed
-
- Blasco MA (2004) Telomere epigenetics: a higher-order control of telomere length in mammalian cells. Carcinogenesis 25: 1083–1087. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100: 57–70. - PubMed
-
- Harley CB, Kim NW, Prowse KR, Weinrich SL, Hirsch KS, et al. (1994) Telomerase, cell immortality and cancer. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 59: 307–315. - PubMed
-
- Dikmen ZG, Gellert GC, Jackson S, Gryaznov S, Tressler R, et al. (2005) In vivo inhibition of lung cancer by GRN163L: A novel human telomerase inhibitor. Cancer Research 65: 7866–7873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

