Differential microRNA profiling in a cellular hypoxia reoxygenation model upon posthypoxic propofol treatment reveals alterations in autophagy signaling network
- PMID: 24454982
- PMCID: PMC3885199
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/378484
Differential microRNA profiling in a cellular hypoxia reoxygenation model upon posthypoxic propofol treatment reveals alterations in autophagy signaling network
Abstract
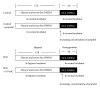
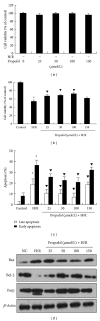
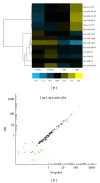
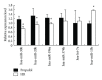
Recent studies indicate that propofol may protect cells via suppressing autophagic cell death caused by excessive reactive oxygen species induced by hypoxia reoxygenation (H/R). It is established that gene expression patterns including autophagy-related genes changed significantly during the process of H/R in the presence or absence of propofol posthypoxia treatment (P-PostH). The reasons for such differences, however, remain largely unknown. MicroRNAs provide a novel mechanism for gene regulation. In the present study, we systematically analyzed the alterations in microRNA expression using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) subjected to H/R in the presence or absence of posthypoxic propofol treatment. Genome-wide profiling of microRNAs was then conducted using microRNA microarray. Fourteen miRNAs are differentially expressed and six of them were validated by the quantitative real-time PCR (Q-PCR) of which three were substantially increased, whereas one was decreased. To gain an unbiased global perspective on subsequent regulation by altered miRNAs, predicted targets of ten miRNAs were analyzed using the Gene Ontology (GO) analysis to build signaling networks. Interestingly, six of the identified microRNAs are known to target autophagy-related genes. In conclusion, our results revealed that different miRNA expression patterns are induced by propofol posthypoxia treatment in H/R and the alterations in miRNA expression patterns are implicated in regulating distinctive autophagy-related gene expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Propofol-induced MiR-20b expression initiates endogenous cellular signal changes mitigating hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced endothelial autophagy in vitro.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 13;11(8):681. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02828-9. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32826852 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-20b-5p regulates propofol-preconditioning-induced inhibition of autophagy in hypoxia-and-reoxygenation-stimulated endothelial cells.J Biosci. 2020;45:35. J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32098914
-
Propofol Upregulates MicroRNA-30b to Inhibit Excessive Autophagy and Apoptosis and Attenuates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury In Vitro and in Patients.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 30;2022:2109891. doi: 10.1155/2022/2109891. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35401922 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-modulated autophagic signaling networks in cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 May;44(5):733-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.02.004. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22342941 Review.
-
MicroRNAs play an essential role in autophagy regulation in various disease phenotypes.Biofactors. 2019 Nov;45(6):844-856. doi: 10.1002/biof.1555. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Biofactors. 2019. PMID: 31418958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Propofol-induced MiR-20b expression initiates endogenous cellular signal changes mitigating hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced endothelial autophagy in vitro.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 13;11(8):681. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02828-9. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32826852 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahydrobiopterin Protects against Radiation-induced Growth Inhibition in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Nov 20;129(22):2733-2740. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.193455. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 27824007 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA SCIRT Promotes HUVEC Angiogenesis via Stabilizing VEGFA mRNA Induced by Hypoxia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 3;2022:9102978. doi: 10.1155/2022/9102978. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35698607 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-20b-5p regulates propofol-preconditioning-induced inhibition of autophagy in hypoxia-and-reoxygenation-stimulated endothelial cells.J Biosci. 2020;45:35. J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32098914
-
Crucial role of autophagy in propofol-treated neurological diseases: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Oct 25;17:1274727. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1274727. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37946715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eltzschig HK, Collard CD. Vascular ischaemia and reperfusion injury. British Medical Bulletin. 2004;70:71–86. - PubMed
-
- Huang Z, Zhong X, Irwin MG, et al. Synergy of isoflurane preconditioning and propofol postconditioning reduces myocardial reperfusion injury in patients. Clinical Science. 2011;121(2):57–69. - PubMed
-
- Hughes SF, Cotter MJ, Evans SA, Jones KP, Adams RA. Role of leucocytes in damage to the vascular endothelium during ischaemia-reperfusion injury. British Journal of Biomedical Science. 2006;63(4):166–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

