Persistence and progression of masked hypertension: a 5-year prospective study
- PMID: 24455208
- PMCID: PMC3877639
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/836387
Persistence and progression of masked hypertension: a 5-year prospective study
Abstract
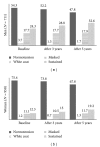
Objectives. To examine masked hypertension persistence over 5 years. Methods. White-collar workers were recruited from three public organizations. Blood pressure (BP) was measured using Spacelabs 90207. Manually operated BP was defined as the mean of the first three readings taken at rest. Ambulatory BP was defined as the mean of the next readings taken every 15 minutes and recorded during working hours. BP was assessed three times over 5 years. Masked hypertension was defined as manually operated BP less than 140 and less than 90 mmHg and ambulatory BP at least 135 or at least 85 mmHg. Sustained hypertension was defined as manually operated BP at least 140 or at least 90 mmHg and ambulatory BP at least 135 or at least 85 mmHg or being treated for hypertension. Results. BP measurements were obtained from 1669 participants from whom 232 had masked hypertension at baseline. Persistence of masked hypertension was 38% and 18.5%, after 3 and 5 years, respectively. Progression to sustained hypertension was 26% and 37%, after 3 and 5 years, respectively. Conclusion. Among baseline masked hypertensives, one-third progressed to sustained hypertension and about one out of five remained masked after 5 years, potentially delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long Working Hours and the Prevalence of Masked and Sustained Hypertension.Hypertension. 2020 Feb;75(2):532-538. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.12926. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 31852264
-
Masked hypertension: different blood pressure measurement methodology and risk factors in a working population.J Hypertens. 2009 Aug;27(8):1560-7. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832cb036. J Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19444141
-
Masked hypertension and effort-reward imbalance at work among 2369 white-collar workers.J Hum Hypertens. 2017 Oct;31(10):620-626. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2017.42. Epub 2017 Jun 22. J Hum Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28639611
-
[Masked hypertension: myth or reality?].Presse Med. 2008 Jun;37(6 Pt 2):1034-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2008.01.022. Epub 2008 May 2. Presse Med. 2008. PMID: 18450414 Review. French.
-
Masked hypertension: a review.Hypertens Res. 2007 Jun;30(6):479-88. doi: 10.1291/hypres.30.479. Hypertens Res. 2007. PMID: 17664850 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolated Nocturnal Hypertension in Children.Front Pediatr. 2022 Feb 18;10:823414. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.823414. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35252065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The importance of masked hypertension in adults with prehypertension.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Aug;12(8):497. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.100. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26149482 No abstract available.
-
Ambulatory blood pressure phenotypes and the risk for hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014 Oct;16(10):481. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0481-5. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014. PMID: 25139779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations of blood pressure with common factors among left-behind farmers in rural China: a cross-sectional study using quantile regression analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Jan;94(2):e142. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000142. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25590833 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of masked uncontrolled hypertension detected through home blood pressure monitoring.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019 Jul;21(7):877-883. doi: 10.1111/jch.13596. Epub 2019 Jun 19. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019. PMID: 31215143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pickering TG, Davidson K, Gerin W, Schwartz JE. Masked hypertension. Hypertension. 2002;40(6):795–796. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien E, Asmar R, Beilin L, et al. Practice guidelines of the European Society of Hypertension for clinic, ambulatory and self blood pressure measurement. Journal of Hypertension. 2005;23(4):697–701. - PubMed
-
- Fagard RH, Cornelissen VA. Incidence of cardiovascular events in white-coat, masked and sustained hypertension versus true normotension: a meta-analysis. Journal of Hypertension. 2007;25(11):2193–2198. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Dov IZ, Ben-Arie L, Mekler J, Bursztyn M. Reproducibility of white-coat and masked hypertension in ambulatory BP monitoring. International Journal of Cardiology. 2007;117(3):355–359. - PubMed
-
- Lurbe E, Torro I, Alvarez V, et al. Prevalence, persistence, and clinical significance of masked hypertension in youth. Hypertension. 2005;45(4):493–498. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources