Design and characterization of double layered mucoadhesive system containing bisphosphonate derivative
- PMID: 24455313
- PMCID: PMC3880750
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/604690
Design and characterization of double layered mucoadhesive system containing bisphosphonate derivative
Abstract
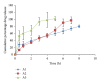
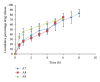
The objective of this study is to evaluate the effect of formulation variables on different evaluation properties such as cumulative percentage release and swelling index in development of two layered buccal mucoadhesive system consisting of a highly water soluble drug risedronate sodium. The mucoadhesive systems were developed with varied concentrations of the polymers (1-2%) using plasticizer/permeation enhancer (25-50% w/w of polymer). Two layered films comprised of risedronate sodium with chitosan (85% deacetylated) and hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose (HPMC 4KM) interpolymer complex of different ratios were prepared by solvent casting method. An impermeable backing membrane of ethyl cellulose was incorporated into the films. The study shows the effect of multipolymeric films on the release of a bisphosphonates derivative. The optimized formulations showed films with uniform drug content (90.91 ± 0.17-105.53% ± 2.15), thickness (0.22 ± 0.01 mm to 0.31 ± 0.06 mm), mucoadhesivity (26 ± 3.61-42.33 ± 2.82 g), and controlled drug release profile up to a period of 10 hours. The films were also studied for swelling index, moisture uptake, viscosity, folding endurance, water vapor transmission rate, and mucoadhesive time.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Design, Development and In vitro/Ex vivo Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Buccal Film of Benzydamine Hydrochloride for the Effective Treatment of Aphthous Stomatitis.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018;12(4):277-294. doi: 10.2174/1872211313666190128151038. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018. PMID: 30706830
-
Formulation and evaluation of mucoadhesive buccal films of enalapril maleate.Indian J Pharm Sci. 2010 Sep;72(5):571-5. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.78522. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2010. PMID: 21694987 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and pharmaceutical evaluation of glibenclamide slow release mucoadhesive buccal film.Res Pharm Sci. 2014 May-Jun;9(3):213-23. Res Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 25657792 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of bone microarchitecture in methylprednisolone induced rat model of osteoporosis by using thiolated chitosan-based risedronate mucoadhesive film.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018 Nov;44(11):1845-1856. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2018.1503297. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30028215
-
Mucoadhesive buccal films of glibenclamide: Development and evaluation.Int J Pharm Investig. 2011 Jan;1(1):42-7. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.76728. Int J Pharm Investig. 2011. PMID: 23071919 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A mini-review on drug delivery through wafer technology: Formulation and manufacturing of buccal and oral lyophilizates.J Adv Res. 2019 May 3;20:33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2019.04.010. eCollection 2019 Nov. J Adv Res. 2019. PMID: 31193385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid Dispersions Incorporated into PVP Films for the Controlled Release of Trans-Resveratrol: Development, Physicochemical and In Vitro Characterizations and In Vivo Cutaneous Anti-Inflammatory Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 27;14(6):1149. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061149. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745722 Free PMC article.
-
Gellan Gum-Based Bilayer Mucoadhesive Films Loaded with Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride and Clove Oil for Possible Treatment of Periodontitis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Sep 16;15:3937-3952. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S328722. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34556975 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylcellulose-A Pharmaceutical Excipient with Multidirectional Application in Drug Dosage Forms Development.Materials (Basel). 2019 Oct 17;12(20):3386. doi: 10.3390/ma12203386. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31627271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Box-Behnken Design in the Preparation, Optimization, and In-Vivo Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Oral Tadalafil-Loaded Niosomal Film.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 3;15(1):173. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010173. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perumal VA, Lutchman D, Mackraj I, Govender T. Formulation of monolayered films with drug and polymers of opposing solubilities. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2008;358(1-2):184–191. - PubMed
-
- Patel VM, Prajapati BG, Patel MM. Design and characterization of chitosan-containing mucoadhesive buccal patches of propranolol hydrochloride. Acta Pharmaceutica. 2007;57(1):61–72. - PubMed
-
- Morales JO, McConville JT. Manufacture and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal films. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. 2011;77(2):187–199. - PubMed
-
- Attama AA, Akpa PA, Onugwu LE, Igwilo G. Novel buccoadhesive delivery system of hydrochlorothiazide formulated with ethyl cellulose-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose interpolymer complex. Scientific Research and Essays. 2008;3(8):343–347.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

