Successful Use of Higher-Dose Etanercept for Multirefractory Systemic Flare of Adult-Onset Still's Disease with Liver Failure with No Response to Tocilizumab Therapy
- PMID: 24455384
- PMCID: PMC3877607
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/923497
Successful Use of Higher-Dose Etanercept for Multirefractory Systemic Flare of Adult-Onset Still's Disease with Liver Failure with No Response to Tocilizumab Therapy
Abstract
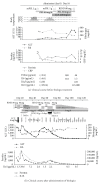
A 21-year-old woman with refractory systemic flare of adult-onset Still's disease with liver failure despite high-dose corticosteroids, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, and tocilizumab, was successfully treated with additional use of etanercept. Etanercept at a dose of 50 mg weekly was partially effective but could not reduce the dose of concomitant betamethasone from 5 mg/day. Etanercept at a dose of 75 mg weekly could lead her to clinical remission and enabled successful tapering off the corticosteroids and discontinuation of etanercept. Normalization of serum C-reactive protein and interleukin 6 and persistent elevation of serum tumor necrosis factor α under the treatment with high-dose corticosteroids and immunosuppressants suggest that tumor necrosis factor α was more deeply involved than at least interleukin 6 in the pathogenesis of refractoriness of the disease in this patient, and these findings might be indicative of potential efficacy for adjunctive use of a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor rather than an interleukin 6 inhibitor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Case report: successful use of short-term add-on tocilizumab for multirefractory systemic flare of adult-onset Still's disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2013 Mar;32 Suppl 1:S103-6. doi: 10.1007/s10067-010-1562-8. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Clin Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 20842515
-
[Biological treatment in severe Still's disease--a case report].Wiad Lek. 2015;68(1):104-7. Wiad Lek. 2015. PMID: 26094343 Polish.
-
Glucocorticoid and cyclosporine refractory adult onset Still's disease successfully treated with tocilizumab.Clin Rheumatol. 2009 Apr;28(4):485-7. doi: 10.1007/s10067-009-1097-z. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19184270
-
A case of refractory adult-onset Still's disease successfully controlled with tocilizumab and a review of the literature.Clin Rheumatol. 2010 Dec;29(12):1465-7. doi: 10.1007/s10067-010-1553-9. Epub 2010 Aug 24. Clin Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20734215 Review.
-
Tocilizumab in refractory adult-onset Still's disease with aseptic meningitis--efficacy of interleukin-6 blockade and review of the literature.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Feb;40(4):365-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2010.05.003. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 20621335 Review.
Cited by
-
Adult-Onset Still's Disease: Still a Serious Health Problem (a Case Report and Literature Review).Am J Case Rep. 2017 Feb 3;18:119-124. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.901846. Am J Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28154368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tocilizumab for uncontrollable systemic inflammatory response syndrome complicating adult-onset Still disease: Case report and review of literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jul;96(29):e7596. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007596. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28723802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of adult-onset Still's disease: evidence- and consensus-based recommendations by experts.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 May 3;63(6):1656-1663. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead461. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37669122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Efthimiou P, Georgy S. Pathogenesis and management of adult-onset still’s disease. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2006;36(3):144–152. - PubMed
-
- Félix FHC, Leal LKAM, Fontenele JB. Cloak and dagger: the case for adult onset still disease and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Rheumatology International. 2009;29(8):973–974. - PubMed
-
- Ogata A, Kitano M, Yamanaka J, et al. Interleukin 18 and hepatocyte growth factor in fulminant hepatic failure of adult onset Still’s disease. Journal of Rheumatology. 2003;30(5):1093–1096. - PubMed
-
- De Bandt M, Saint-Marcoux B. Tocilizumab for multirefractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2009;68(1):153–154. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

