Adipose tissue in obesity-related inflammation and insulin resistance: cells, cytokines, and chemokines
- PMID: 24455420
- PMCID: PMC3881510
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/139239
Adipose tissue in obesity-related inflammation and insulin resistance: cells, cytokines, and chemokines
Abstract
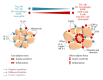
Adipose tissue is a complex organ that comprises a wide range of cell types with diverse energy storage, metabolic regulation, and neuroendocrine and immune functions. Because it contains various immune cells, either adaptive (B and T lymphocytes; such as regulatory T cells) or innate (mostly macrophages and, more recently identified, myeloid-derived suppressor cells), the adipose tissue is now considered as a bona fide immune organ, at the cross-road between metabolism and immunity. Adipose tissue disorders, such as those encountered in obesity and lipodystrophy, cause alterations to adipose tissue distribution and function with broad effects on cytokine, chemokine, and hormone expression, on lipid storage, and on the composition of adipose-resident immune cell populations. The resulting changes appear to induce profound consequences for basal systemic inflammation and insulin sensitivity. The purpose of this review is to synthesize the current literature on adipose cell composition remodeling in obesity, which shows how adipose-resident immune cells regulate inflammation and insulin resistance-notably through cytokine and chemokine secretion-and highlights major research questions in the field.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical