Comparative evaluation of NovaMin desensitizer and Gluma desensitizer on dentinal tubule occlusion: a scanning electron microscopic study
- PMID: 24455439
- PMCID: PMC3891858
- DOI: 10.5051/jpis.2013.43.6.269
Comparative evaluation of NovaMin desensitizer and Gluma desensitizer on dentinal tubule occlusion: a scanning electron microscopic study
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, the effect of calcium sodium phosphosilicate (NovaMin) desensitizing agent, which is a powder-based system, and hydroxyethyl methacrylate and glutaraldehyde (Gluma desensitizer), which is liquid-based system, on dentinal tubule occlusion was analyzed by scanning electron microscope. The effects of the above two along with one control group were compared to determine the more effective method of sealing the dentinal tubules after initial application.
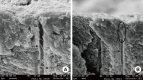
Methods: Twenty specimens were allocated to each of 3 groups: Control, Gluma desensitizer, and NovaMin. Two additional samples were also prepared and treated with Gluma and NovaMin; these samples were longitudinally fractured. The specimens were prepared from extracted sound human premolars and were stored in 10% formalin at room temperature. The teeth were cleaned of gross debris and then sectioned to provide one to two dentin specimens. The dentin specimens were etched with 6% citric acid for 2 minutes and rinsed in distilled water. Control discs were dried, and the test discs were treated with the desensitizing agents as per the manufacturer's instructions. The discs as well as longitudinal sections were later analyzed under the scanning electron microscope. The proportions of completely occluded, partially occluded, and open tubules within each group were calculated. The ratios of completely and partially occluded tubules to the total tubules for all the groups was determined, and the data was statistically analyzed using nonparametric tests and statistical significance was calculated.
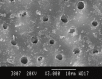
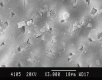
Results: NovaMin showed more completely occluded tubules (0.545±0.051) while Gluma desensitizer showed more partially occluded tubules (0.532±0.075). The differences among all the groups were statistically significant (P≤ 0.05).
Conclusion: Both materials were effective in occluding dentinal tubules but NovaMin appeared more promising in occluding tubules completely after initial application.
Keywords: Dentin sensitivity; Gluma desensitizer; NovaMin; Scanning electron microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Occluding effect of Nd:YAG laser and different dentin desensitizing agents on human dentinal tubules in vitro: a scanning electron microscopy investigation.Oper Dent. 2012 Jul-Aug;37(4):340-55. doi: 10.2341/10-188-L. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Oper Dent. 2012. PMID: 22313266 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Durability of Two Desensitizing Agents on Dentinal Tubule Occlusion: An In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2024 Nov 21;16(11):e74189. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74189. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39712797 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of different desensitizers and lasers on dentine tubules: An in-vitro analysis.Microsc Res Tech. 2017 Jul;80(7):737-744. doi: 10.1002/jemt.22859. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Microsc Res Tech. 2017. PMID: 28251725
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Three Commercially Available Desensitizing Mouthwash on Dentinal Tubule Occlusion: An In Vitro Scanning Electron Microscopic Study.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2023 Oct 30;13(5):426-432. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_97_23. eCollection 2023 Sep-Oct. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2023. PMID: 38124731 Free PMC article.
-
Scanning electron microscopy evaluation of the link between a new dentinal desensitizer and dentine.Minerva Stomatol. 2003 Sep;52(9):413-21, 421-5. Minerva Stomatol. 2003. PMID: 14608247 Review. English, Italian.
Cited by
-
Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of the desensitizing and remineralizing agent in the reduction of dentin hypersensitivity after orthodontic debonding - a randomized clinical trial.Med Pharm Rep. 2021 Apr;94(2):229-238. doi: 10.15386/mpr-1763. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Med Pharm Rep. 2021. PMID: 34013195 Free PMC article.
-
Penetration and durability of CPP-ACP paste and sodium fluoride varnish as desensitizing agents: An in vitro comparison.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2023 Spring;17(2):119-127. doi: 10.34172/joddd.2023.28050. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2023. PMID: 37649823 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of ex vivo effectiveness of commercial desensitizing dentifrices.J Clin Exp Dent. 2017 Apr 1;9(4):e503-e510. doi: 10.4317/jced.53040. eCollection 2017 Apr. J Clin Exp Dent. 2017. PMID: 28469813 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of fluoride-containing toothpastes associated with different technologies to remineralize enamel after pH cycling: an in vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Nov 14;22(1):489. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02429-2. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36376830 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of retention of cast crown luted with glass ionomer cement in presence of two different types of desensitizer agent on extracted teeth-an in vitro study.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 6;10(3):e25891. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25891. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38371974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banoczy J. Dentine hypersensitivity: general practice considerations for successful management. Int Dent J. 2002;52(Suppl 5):366.
-
- Johnson RH, Zulqar-Nain BJ, Koval JJ. The effectiveness of an electro-ionizing toothbrush in the control of dentinal hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1982;53:353–359. - PubMed
-
- Curro FA. Tooth hypersensitivity in the spectrum of pain. Dent Clin North Am. 1990;34:429–437. - PubMed
-
- Bamise CT, Olusile AO, Oginni AO. An analysis of the etiological and predisposing factors related to dentin hypersensitivity. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2008;9:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Dababneh RH, Khouri AT, Addy M. Dentine hypersensitivity - an enigma? A review of terminology, mechanisms, aetiology and management. Br Dent J. 1999;187:606–611. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

