Role of redox signaling in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 24455696
- PMCID: PMC3884773
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/484613
Role of redox signaling in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
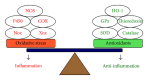
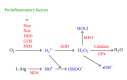
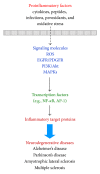
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), a redox signal, are produced by various enzymatic reactions and chemical processes, which are essential for many physiological functions and act as second messengers. However, accumulating evidence has implicated the pathogenesis of several human diseases including neurodegenerative disorders related to increased oxidative stress. Under pathological conditions, increasing ROS production can regulate the expression of diverse inflammatory mediators during brain injury. Elevated levels of several proinflammatory factors including cytokines, peptides, pathogenic structures, and peroxidants in the central nervous system (CNS) have been detected in patients with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). These proinflammatory factors act as potent stimuli in brain inflammation through upregulation of diverse inflammatory genes, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and adhesion molecules. To date, the intracellular signaling mechanisms underlying the expression of target proteins regulated by these factors are elusive. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms underlying the intracellular signaling pathways, especially ROS, involved in the expression of several inflammatory proteins induced by proinflammatory factors in brain resident cells. Understanding redox signaling transduction mechanisms involved in the expression of target proteins and genes may provide useful therapeutic strategies for brain injury, inflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Rahman I, Marwick J, Kirkham P. Redox modulation of chromatin remodeling: impact on histone acetylation and deacetylation, NF-κB and pro-inflammatory gene expression. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2004;68(6):1255–1267. - PubMed
-
- Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. International Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. 2007;39(1):44–84. - PubMed
-
- Lee IT, Yang CM. Role of NADPH oxidase/ROS in pro-inflammatory mediators-induced airway and pulmonary diseases. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2012;84(5):581–590. - PubMed
-
- Dröge W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiological Reviews. 2002;82(1):47–95. - PubMed
-
- von Bernhardi R, Eugenín J. Alzheimer’s disease: redox dysregulation as a common denominator for diverse pathogenic mechanisms. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2012;16(9):974–1031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

