Effects of acute exercise and chronic exercise on the liver leptin-AMPK-ACC signaling pathway in rats with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 24455748
- PMCID: PMC3877642
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/946432
Effects of acute exercise and chronic exercise on the liver leptin-AMPK-ACC signaling pathway in rats with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of acute and chronic exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism in liver of rats with type 2 diabetes caused by a high fat diet and low dose streptozotocin (STZ).
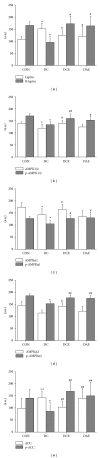
Methods: Animals were classified into control (CON), diabetes (DC), diabetic chronic exercise (DCE), and diabetic acute exercise (DAE) groups.
Results: Compared to CON, the leptin levels in serum and liver and ACC phosphorylation were significantly higher in DC, but the levels of liver leptin receptor, AMPK α 1/2, AMPK α 1, and ACC proteins expression and phosphorylation were significantly lower in DC. In addition, the levels of liver glycogen reduced significantly, and the levels of TG and FFA increased significantly in DC compared to CON. Compared to DC, the levels of liver AMPK α 1/2, AMPK α 2, AMPK α 1, and ACC phosphorylation significantly increased in DCE and DAE. However, significant increase of the level of liver leptin receptor and glycogen as well as significant decrease of the level of TG and FFA were observed only in DEC.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that both acute and chronic exercise indirectly activated the leptin-AMPK-ACC signaling pathway and increased insulin sensitivity in the liver of type 2 diabetic rats. However, only chronic and long-term exercise improved glucose and lipid metabolism of the liver.
Figures

References
-
- Oral EA, Simha V, Ruiz E, et al. Leptin-replacement therapy for lipodystrophy. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;346(8):570–578. - PubMed
-
- Friedman JM. Modern science versus the stigma of obesity. Nature Medicine. 2004;10(6):563–569. - PubMed
-
- Mapfei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nature Medicine. 1995;1(11):1155–1161. - PubMed
-
- Widjaja A, Stratton IM, Horn R, Holman RR, Turner R, Brabant G. UKPDS 20: plasma leptin, obesity, and plasma insulin in type 2 diabetic subjects. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 1997;82(2):654–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

