Reverse micelles as a platform for dynamic nuclear polarization in solution NMR of proteins
- PMID: 24456213
- PMCID: PMC3955360
- DOI: 10.1021/ja4107176
Reverse micelles as a platform for dynamic nuclear polarization in solution NMR of proteins
Abstract
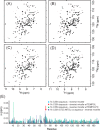
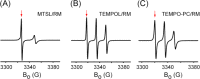
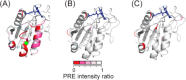
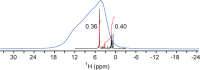
Despite tremendous advances in recent years, solution NMR remains fundamentally restricted due to its inherent insensitivity. Dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) potentially offers significant improvements in this respect. The basic DNP strategy is to irradiate the EPR transitions of a stable radical and transfer this nonequilibrium polarization to the hydrogen spins of water, which will in turn transfer polarization to the hydrogens of the macromolecule. Unfortunately, these EPR transitions lie in the microwave range of the electromagnetic spectrum where bulk water absorbs strongly, often resulting in catastrophic heating. Furthermore, the residence times of water on the surface of the protein in bulk solution are generally too short for efficient transfer of polarization. Here we take advantage of the properties of solutions of encapsulated proteins dissolved in low viscosity solvents to implement DNP in liquids. Such samples are largely transparent to the microwave frequencies required and thereby avoid significant heating. Nitroxide radicals are introduced into the reverse micelle system in three ways: attached to the protein, embedded in the reverse micelle shell, and free in the aqueous core. Significant enhancements of the water resonance ranging up to ∼-93 at 0.35 T were observed. We also find that the hydration properties of encapsulated proteins allow for efficient polarization transfer from water to the protein. These and other observations suggest that merging reverse micelle encapsulation technology with DNP offers a route to a significant increase in the sensitivity of solution NMR spectroscopy of proteins and other biomolecules.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reverse Micelle Encapsulation of Proteins for NMR Spectroscopy.Methods Enzymol. 2019;615:43-75. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2018.08.032. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Methods Enzymol. 2019. PMID: 30638537 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance and electron spin resonance studies of hydration and local water dynamics in micelle and vesicle assemblies.Langmuir. 2008 Sep 16;24(18):10062-72. doi: 10.1021/la800334k. Epub 2008 Aug 14. Langmuir. 2008. PMID: 18700788
-
Characterizing Protein Hydration Dynamics Using Solution NMR Spectroscopy.Methods Enzymol. 2019;615:77-101. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2018.09.040. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Methods Enzymol. 2019. PMID: 30638541 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative cw Overhauser effect dynamic nuclear polarization for the analysis of local water dynamics.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2013 Oct;74:33-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2013. PMID: 24083461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-field EPR on membrane proteins - crossing the gap to NMR.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2013 Nov;75:1-49. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2013. PMID: 24160760 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting the DNP-SENS efficiency in reactive heterogeneous catalysts from hydrophilicity.Chem Sci. 2018 Apr 30;9(21):4866-4872. doi: 10.1039/c8sc00532j. eCollection 2018 Jun 7. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 29910939 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse Micelle Encapsulation of Proteins for NMR Spectroscopy.Methods Enzymol. 2019;615:43-75. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2018.08.032. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Methods Enzymol. 2019. PMID: 30638537 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and cost-efficient hyperpolarization of long-lived nuclear spin states on universal (15)N2-diazirine molecular tags.Sci Adv. 2016 Mar 25;2(3):e1501438. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501438. eCollection 2016 Mar. Sci Adv. 2016. PMID: 27051867 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Biocompatibility for a Hydrophilic Biological Molecule Encapsulation System.Molecules. 2022 Feb 27;27(5):1572. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051572. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268673 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution NMR spectroscopy of encapsulated proteins dissolved in low-viscosity fluids.J Magn Reson. 2014 Apr;241:137-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2013.10.006. J Magn Reson. 2014. PMID: 24656086 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Overhauser A. W. Phys. Rev. 1953, 91, 476–476.
-
- Carver T. R.; Slichter C. P. Phys. Rev. 1956, 102, 975–980.
-
- Hausser D.; Stehlik D. Adv. Magn. Reson. 1968, 3, 79–139.
-
- Müller-Warmuth W.; Meise-Gresch K. Adv. Magn. Reson. 1963, 11, 1–45.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

