Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers to predict response of Berberine in suppressing lung cancer invasion and metastasis
- PMID: 24456611
- PMCID: PMC3944941
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-22
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers to predict response of Berberine in suppressing lung cancer invasion and metastasis
Abstract
Background: The effects of berberine on the metastatic potential of lung cancer cells and its underlying mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. Since epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a cellular process associated with cancer invasion and metastasis, we attempted to investigate the potential use of berberine as an inhibitor of TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal in A549 cells.
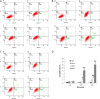
Methods: In this study, we investigated the anticancer activity of berberine against A549 cells in vitro and in vivo. BBR-induced apoptosis of the human lung cancer cells was determined by flow cytometry. The ability of BBR to inhibit TGF-β-induced EMT was examined by QRT-PCR and Western blotting. The impact of BBR on A549 cell migration and invasion was evaluated by transwell assay.
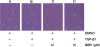
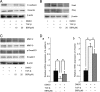
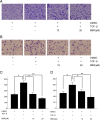
Results: We demonstrated that TGF-β1 induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal to promote lung cancer invasion and metastasis. Berberine inhibited invasion and migration of A549 cells, increased expression of the epithelial phenotype marker E-cadherin, repressed the expression of the mesenchymal phenotype marker Vimentin, as well as decreased the level of epithelial-to-mesenchymal -inducing transcription factors Snail1 and Slug during the initiation of TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal. Furthermore, berberine inhibited growth of lung cancer cells in vivo xenograft.
Conclusions: Our findings provided new evidence that berberine is an effective inhibitor of the metastatic potential of A549 cells through suppression of TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal.
Figures
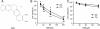
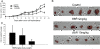
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and suppresses lung cancer invasion and metastasis.Toxicology. 2013 Jan 7;303:139-46. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.09.017. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Toxicology. 2013. PMID: 23146760
-
Berberine Suppresses Cell Motility Through Downregulation of TGF-β1 in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(2):795-807. doi: 10.1159/000487171. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29414799
-
Stereospecific effects of ginsenoside 20-Rg3 inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses lung cancer migration, invasion and anoikis resistance.Toxicology. 2014 Aug 1;322:23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 May 2. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 24793912
-
Berberine as a Potential Anticancer Agent: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2021 Dec 4;26(23):7368. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237368. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berberine: A multifaceted agent for lung cancer treatment-from molecular insight to clinical applications.Gene. 2025 Jan 20;934:149021. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.149021. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39427827 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting of sonic hedgehog-Gli signaling: A potential therapeutic target for patients with breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2016 Aug;12(2):1027-1033. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4722. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27446389 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Lung Carcinogenesis from a Morphostatic Perspective: Prevention and Therapeutic Potential of Phytochemicals for Targeting Cancer Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 27;22(11):5697. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115697. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multidrug-resistant cancer cells and cancer stem cells hijack cellular systems to circumvent systemic therapies, can natural products reverse this?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Mar;74(5):777-801. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2362-3. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27622244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naturally occurring anti-cancer compounds: shining from Chinese herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2019 Nov 6;14:48. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0270-9. eCollection 2019. Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31719837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Implications of TGFβ in Cancer Treatment: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 20;13(3):379. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030379. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33498521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

